September 25, 2006 Chapter 1: Overview
LTPE-UM-3159-02 1-7
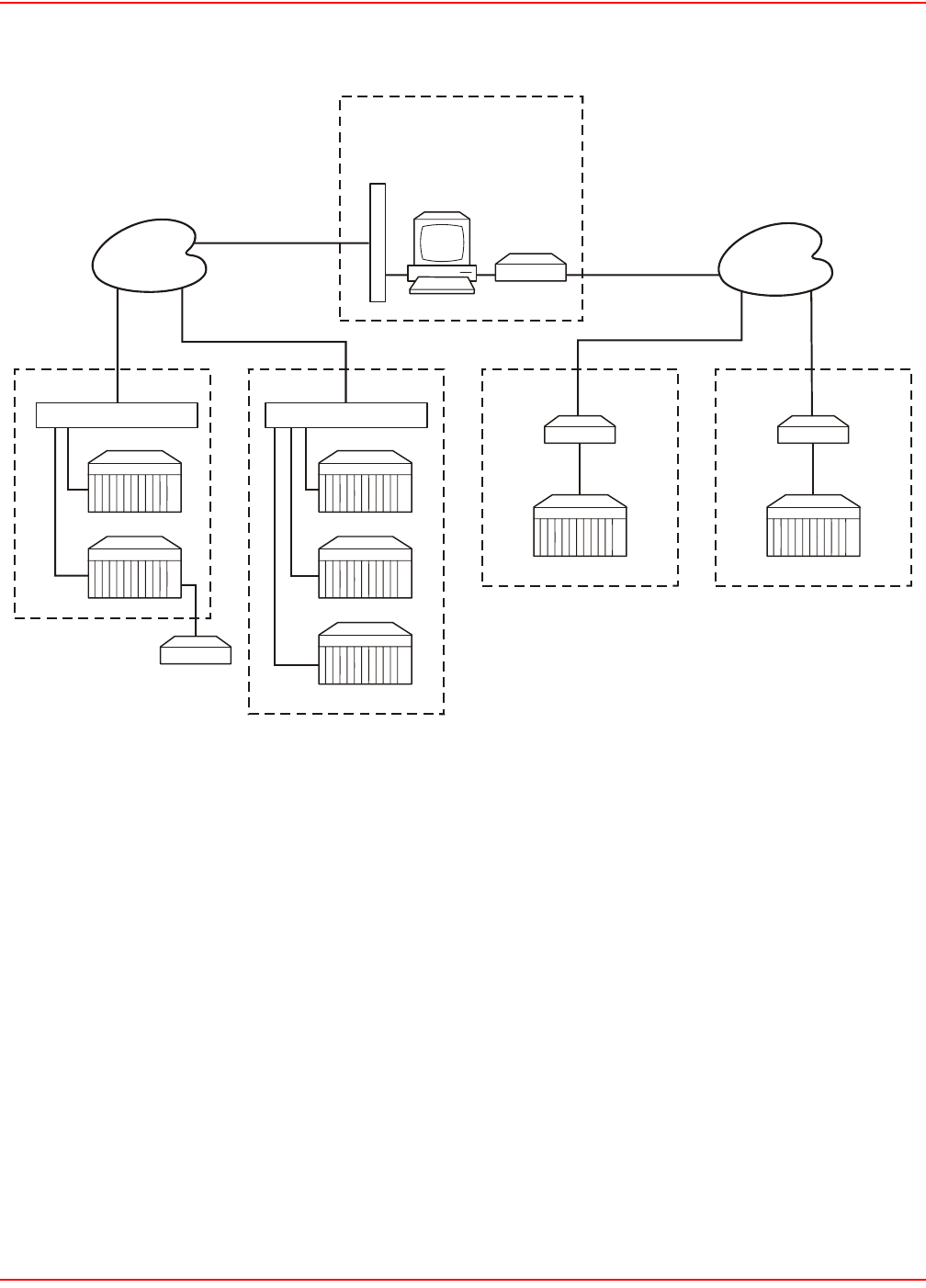
Figure 1-6. WorldDSL Shelves Managed by SNMP through LAN and SNMP through SLIP
SNMP MANAGEMENT INFORMATION BASE
Simple Network Manage Protocol (SNMP) specifies how to send information between a network management
station and managed devices on a network. Managed devices run a program called an agent. The agent interprets
SNMP requests and responds to them. The management station communicates with the agents in the managed
devices to:
• set configurations
• read configurations
• read status parameters
Management Information Bases (MIBs) define these configurations and status parameters. The Internet
Engineering Task Force (IETF) specifies standard MIBs for certain types of devices, ensuring any generic SNMP
application can manage them. Other vendor-specific MIBs such as those used by ADC, define the configuration,
status, trap, and performance parameters unique to the WorldDSL product line.
The EMU-830 performs as a proxy agent when managing line units. Each managed device has configuration,
status, and statistical information that defines its functionality and operation capabilities.
There are a total of six MIB files that define the SNMP management interface of the ADC WorldDSL product. These
files should be copied into the Network Manager Client MIB Subdirectory. Once copied onto the desired drive they
can be easily accessed by the Network Manager’s MIB compiler. The six MIB files are named as follows:
Site #2
Site #1
NTU/STU-R
Ethernet LAN
Ethernet
Network
Ethernet LAN
Managed DSL
link
SNMP
via
SLIP
WorldDSL Shelf
Network Management Station
Unix workstation or PC running SNMP
Management Station software/StarGazer
Ethernet LAN
Modem
Site #3
Modem
RS-232/485
SLIP Port
WorldDSL Shelf
WorldDSL Shelf
WorldDSL Shelf
WorldDSL Shelf
WorldDSL Shelf
Site #3
Modem
RS-232/485
SLIP Port
WorldDSL Shelf
PSTN
SNMP
via
LAN