• The Fibre Channel RAID Array 8000 (RA8000) midrange departmental
storage subsystem and Fibre Channel Enterprise Storage Array 12000
(ESA12000) house two HSG80 dual-channel controllers. There are
provisions for six UltraSCSI channels.
• Only disk devices attached to the HSG80 Fibre Channel to Six Channel
UltraSCSI Array controller are supported with the TruCluster Server
product.
• No tape devices are supported.
• Tru64 UNIX Version 5.0A limits the number of Fibre Channel targets
to 126.
• Tru64 UNIX Version 5.0A allows up to 255 LUNs per target.
• The HSG80 supports transparent and multiple-bus failover mode when
used in a TruCluster Server Version 5.0A configuration. Multiple-bus
failover is recommended for high availability in a cluster.
• A storage array with dual-redundant HSG80 controllers in transparent
mode failover is two targets and consumes four ports on a switch.
• A storage array with dual-redundant HSG80 controllers in multiple-bus
failover is four targets and consumes 4 ports on a switch.
• Each KGPSA is one target.
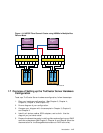
• The HSG80 documentation refers to the controllers as Controllers A (top)
and B (bottom). Each controller provides two ports (left and right). (The
HSG80 documentation refers to these ports as Port 1 and 2, respectively.)
In transparent failover mode, only one left port and one right port are
active at any given time.
With transparent failover enabled, assuming that the left port of the top
controller and the right port of the bottom controller are active, if the top
controller fails in such a way that it can no longer properly communicate
with the switch, then its functions will automatically fail over to the
bottom controller (and vice versa).
• In transparent failover mode, you can configure which controller
presents each HSG80 storage element (unit) to the cluster. Ordinarily,
the left port of either controller serves the units designated D0 through
D99, and the right port serves those designated D100 through D199.
• In multiple-bus failover mode, all units (D0 through D199) are visible to
all host ports, but accessible only through one controller at any specific
time. The host can control the failover process by moving unit(s) from
one controller to the other controller.
Hardware Requirements and Restrictions 2–5