PowerConnect B-Series FCX Configuration Guide 1221
53-1002266-01
How 802.1X port security works
34
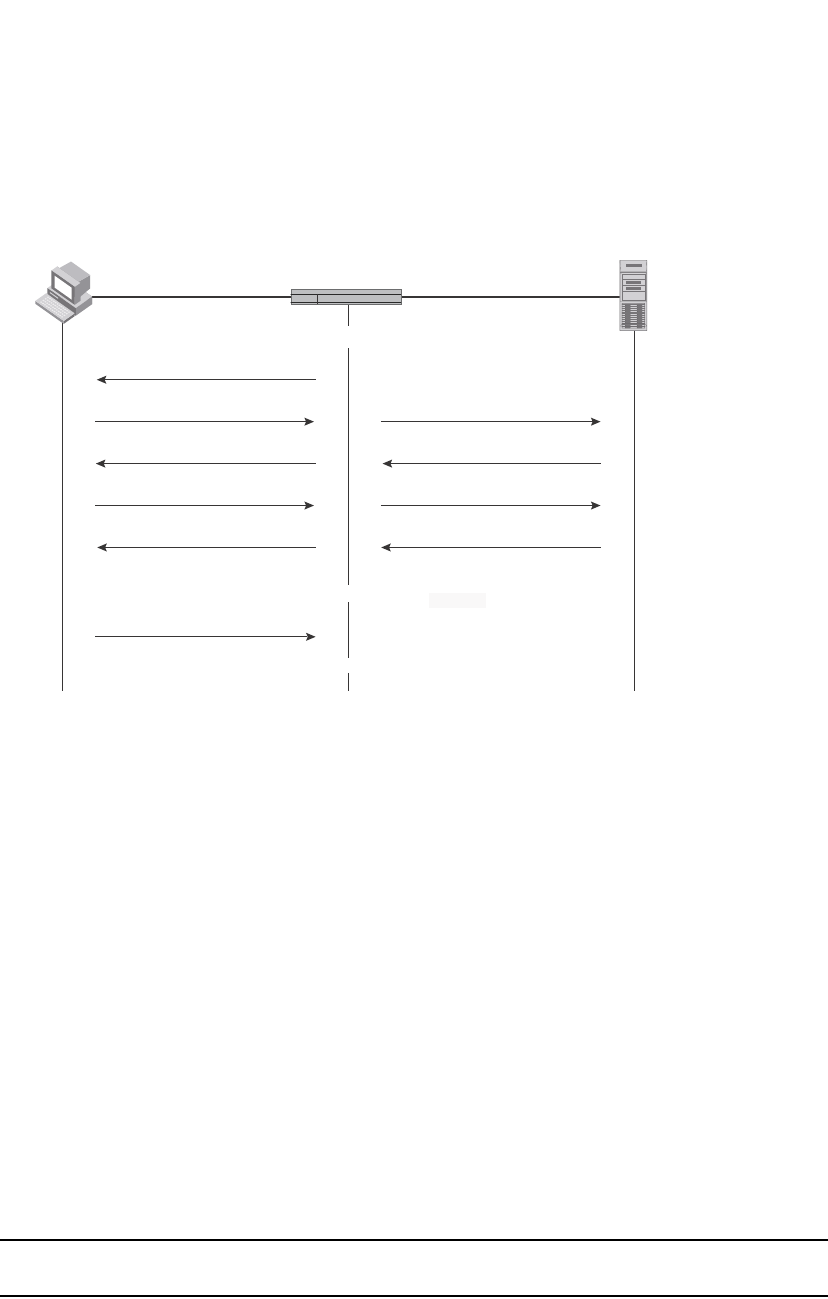
FIGURE 156 Message exchange between client/supplicant, authenticator, and authentication
server
In this example, the Authenticator (the PowerConnect switch) initiates communication with an
802.1X-enabled Client. When the Client responds, it is prompted for a username (255 characters
maximum) and password. The Authenticator passes this information to the Authentication Server,
which determines whether the Client can access services provided by the Authenticator. When the
Client is successfully authenticated by the RADIUS server, the port is authorized. When the Client
logs off, the port becomes unauthorized again.
The Dell 802.1X implementation supports dynamic VLAN assignment. If one of the attributes in the
Access-Accept message sent by the RADIUS server specifies a VLAN identifier, and this VLAN is
available on the PowerConnect device, the client port is moved from its default VLAN to the
specified VLAN. When the client disconnects from the network, the port is placed back in its
default VLAN.Refer to “Configuring dynamic VLAN assignment for 802.1X ports” on page 1230 for
more information.
If a Client does not support 802.1X, authentication cannot take place. The PowerConnect device
sends EAP-Request/Identity frames to the Client, but the Client does not respond to them.
When a Client that supports 802.1X attempts to gain access through a non-802.1X-enabled port, it
sends an EAP start frame to the PowerConnect device. When the device does not respond, the
Client considers the port to be authorized, and starts sending normal traffic.
PowerConnect devices support Identity and MD5-challenge requests in EAP Request/Response
messages as well as the following 802.1X authentication challenge types:
NOTE
Refer to also “EAP pass-through support” on page 1223.
• EAP-TLS (RFC 2716) – EAP Transport Level Security (TLS) provides strong security by requiring
both client and authentication server to be identified and validated through the use of public
key infrastructure (PKI) digital certificates. EAP-TLS establishes a tunnel between the client
and the authentication server to protect messages from unauthorized users’ eavesdropping
RADIUS Server
(Authentication Server)
Client/Supplicant
Port Unauthorized
EAP-Response/Identity
EAP-Request/Identity
EAP-Response/Identity
EAP-Request/MD5-Challenge
EAP-Success
EAP-Logoff
Port Authorized
Port Unauthorized
RADIUS Access-Request
RADIUS Access-Challenge
RADIUS Access-Request
RADIUS Access-Accept
Switch
(Authenticator)


















