- 716 -
VLAN ID - VLAN ID can be any number in the range of (1 to 3965).
Command Buttons
Submit - Update the switch with the values on this screen. If you want the switch to retain the new
values across a power cycle, you must perform a save.
Delete - Delete an entry of IP Subnet to VLAN mapping.
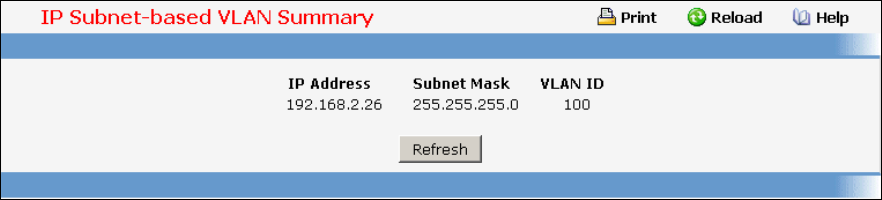
11.3.8.2 Viewing IP Subnet-based VLAN Information Page
Non-Configurable Data
IP Address - The IP Address of the subnet that is being bound to a VLAN ID.
Subnet Mask - Subnet mask of the IP Address bound to VLAN ID.
VLAN ID - VLAN ID to which above mentioned IP Subnet is being bound to. VLAN ID can be any
number in the range of (1 to 3965).
Command Buttons
Refresh - Update the screen with the latest information.
11.3.9 Managing MAC-based VLAN
11.3.9.1 MAC-based VLAN Configuration Page
MAC-based VLAN feature allows incoming untagged packets to be assigned to a VLAN and thus classify
traffic based on the source MAC address of the packet.
A MAC to VLAN mapping is defined by configuring an entry in the MAC to VLAN table. An entry is
specified via a source MAC address and the desired VLAN ID. The MAC to VLAN configurations are
shared across all ports of the device (i.e. there is a system wide table that has MAC address to VLAN ID
mappings).
When untagged or priority tagged packets arrive at the switch and entries exist in the MAC to VLAN table,
the source MAC address of the packet is looked up. If an entry is found the corresponding VLAN ID is
assigned to the packet. If the packet is already priority tagged it will maintain this value, otherwise the
priority will be set to zero. The assigned VLAN ID is verified against the VLAN table, if the VLAN is valid


















