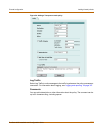
Firewall configuration Adding firewall policies
FortiGate-4000 Installation and Configuration Guide 197
NAT
Configure the policy for NAT. NAT translates the source address and the source port
of packets accepted by the policy. If you select NAT, you can also select Dynamic IP
Pool and Fixed Port. NAT is not available in Transparent mode.
VPN Tunnel
Select a VPN tunnel for an ENCRYPT policy. You can select an AutoIKE key or
Manual Key tunnel. VPN Tunnel is not available in Transparent mode.
Traffic Shaping
Traffic Shaping controls the bandwidth available to and sets the priority of the traffic
processed by the policy. Traffic Shaping makes it possible to control which policies
have the highest priority when large amounts of data are moving through the
FortiGate device. For example, the policy for the corporate web server might be given
higher priority than the policies for most employees’ computers. An employee who
needs unusually high-speed Internet access could have a special outgoing policy set
up with higher bandwidth.
If you set both guaranteed bandwidth and maximum bandwidth to 0 the policy does
not allow any traffic.
Dynamic IP
Pool
Select Dynamic IP Pool to translate the source address to an address
randomly selected from an IP pool. The IP pool must be added to the
destination interface or VLAN subinterface of the policy or to an interface or
VLAN subinterface in the destination zone of the policy.
You cannot select Dynamic IP Pool if the destination interface or VLAN
subinterface is configured using DHCP or PPPoE.
For information about adding IP pools, see “IP pools” on page 218.
Fixed Port Select Fixed Port to prevent NAT from translating the source port. Some
applications do not function correctly if the source port is changed. If you
select Fixed Port, you must also select Dynamic IP Pool and add a dynamic
IP pool address range to the destination interface of the policy. If you do not
select Dynamic IP Pool, a policy with Fixed Port selected can only allow one
connection at a time for this port or service.
Allow inbound Select Allow inbound so that users behind the remote VPN gateway can
connect to the source address.
Allow outbound Select Allow outbound so that users can connect to the destination address
behind the remote VPN gateway.
Inbound NAT Select Inbound NAT to translate the source address of incoming packets to
the FortiGate internal IP address.
Outbound NAT Select Outbound NAT to translate the source address of outgoing packets to
the FortiGate external IP address.