2-92 IBM Informix OnLine Database Server Administrator’s Guide
Structure of a Blobspace or Dbspace Mirror Chunk
Figure 2-15 illustrates the blobspace chunk structure as it appears immedi-
ately after the blobspace is created.
Structure of a Blobspace or Dbspace Mirror Chunk
Each mirror chunk must be the same size as its primary chunk. When a
mirror chunk is created, tbinit schedules a daemon process to immediately
write the contents of the primary chunk to the mirror chunk.
The mirror chunk contains the same control structures as the primary chunk.
A disk space allocation report (tbstat -d) always indicates that a mirror chunk
is full and has no unused pages. Even though the chunk free-list page in the
mirror chunk duplicates the chunk free-list page in the primary chunk, all
OnLine output that describes disk space indicates that the mirror chunk is
100 percent full. The “full” mirror chunk indicates that none of the space in
the chunk is available for use other than as a mirror of the primary chunk.
The status remains full for as long as both primary chunk and mirror chunk
are online.
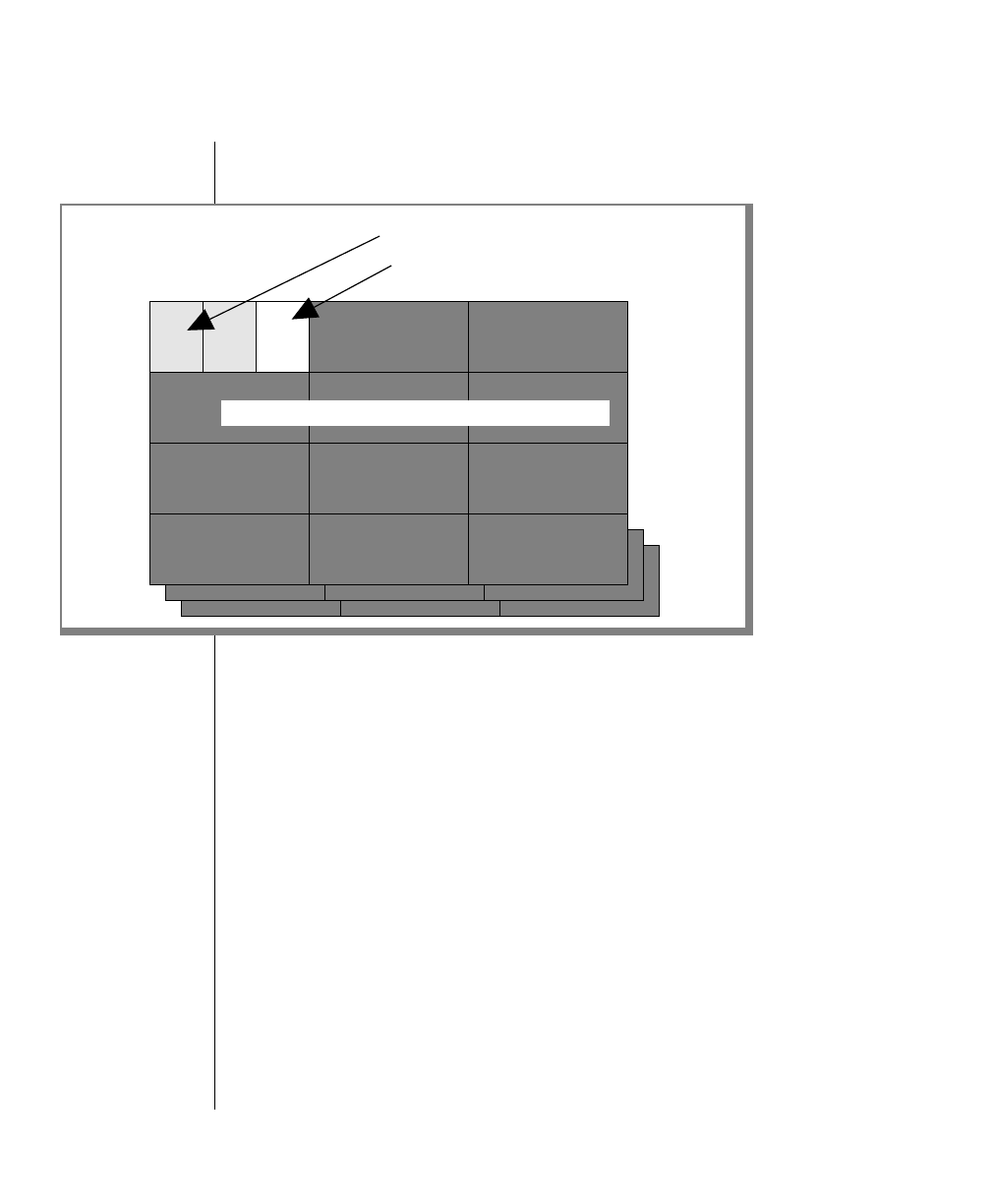
Figure 2-15
Structures within a
blobspace, after the
blobspace is
created. Blobpage
size must be a
multiple of page
size.
Free-map pages
Blobspace
(any chunk)
Unused space initialized as blobpages
Bit map that tracks the free-map pages


















