System Architecture 2-93
OnLine Limits for Chunks
If the primary chunk goes down and the mirror chunk becomes the primary
chunk, disk space allocation reports will accurately describe the fullness of
the new primary chunk.
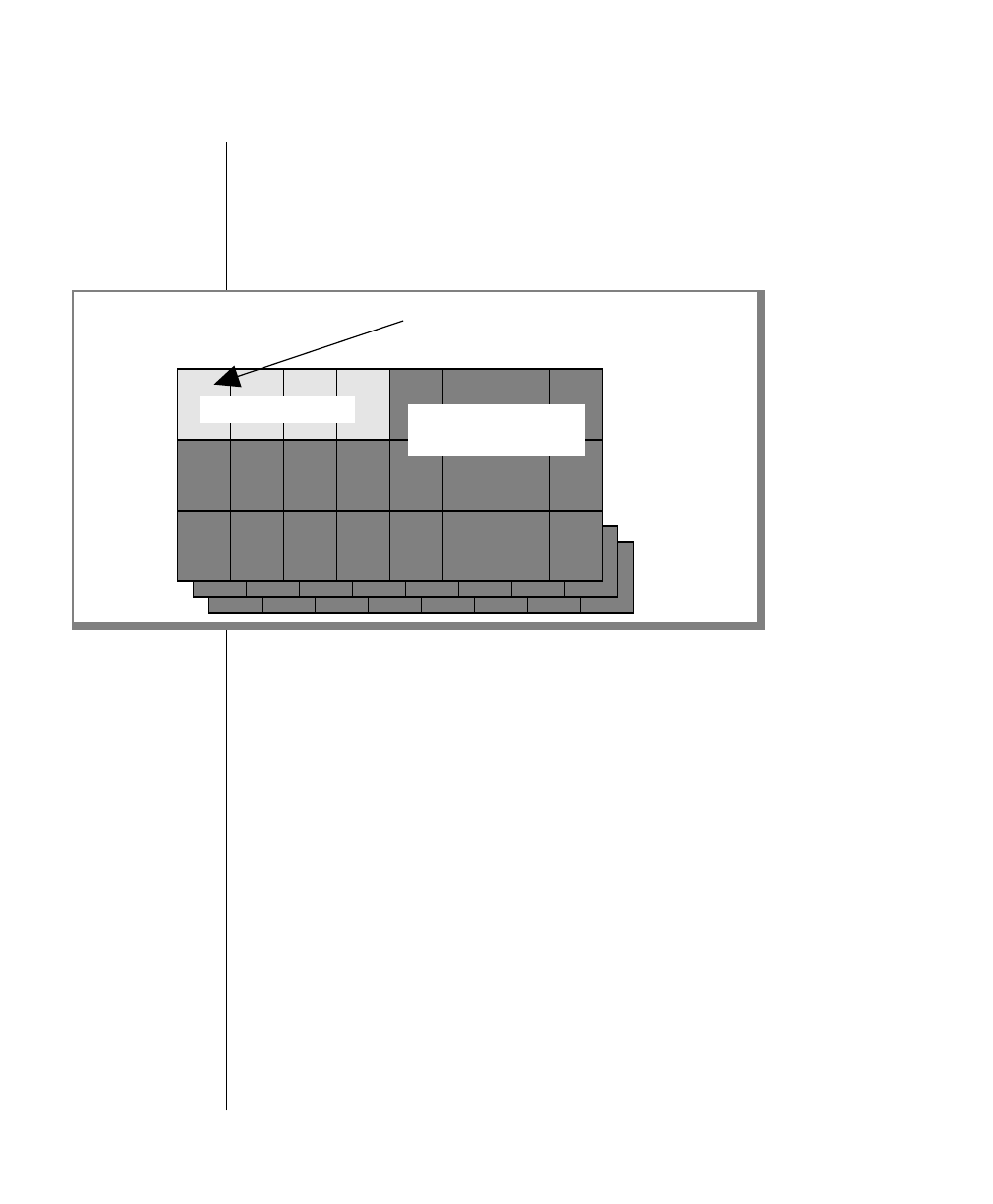
Figure 2-16illustrates themirrorchunk structure as it appears after the chunk
is created.
OnLine Limits for Chunks
The maximum number of chunks that can exist within an OnLine configu-
ration might be operating-system dependent. The maximum value is the
lesser of the following two values:
■ The number of chunk entries (pathnames) that can fit on a page. (Use
tbcheck -pr to display chunk pathnames. Refer to page 2-100.)
■ The maximum number of files a user process can hold open, minus
6. (The maximum number is defined by the operating system.)
OnLine allocates one page for maintaining its list of chunks. OnLine installed
on a machine with a 4-KB page size can accommodate twice as many equal-
sized chunk entries as can an OnLine database server installed on a machine
with a 2-KB page.
Figure 2-16
Structures within a
mirror chunk after
the chunk is
created
Number and type of control pages varies,
depending on chunk type.
Generic mirror
chunk
Remaining space in a mirror
chunk is marked as full.
Control pages


















