Data Consistency, Recovery, and Migration 4-41
Step 1: Checkpoint Condition
Step 1: Checkpoint Condition
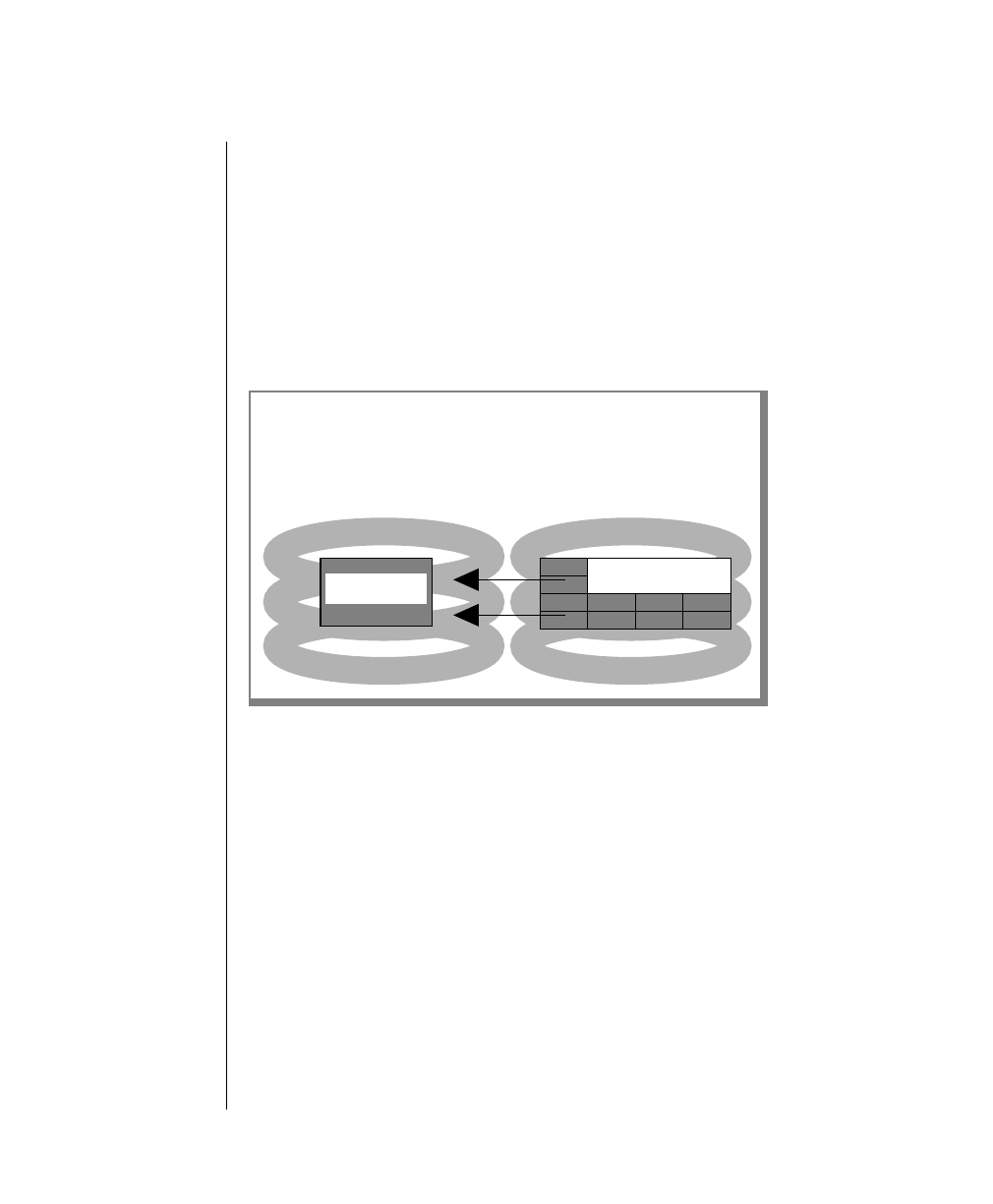
The first step, returning all disk pages to their condition at the time of the
most-recent checkpoint, is accomplished by writing the “before-images”
stored in the physical log back to disk. Each “before-image” in the physical
log contains the address of a page that was updated after the checkpoint. By
writing each “before-image” page in the physical log back to disk, changes to
OnLine data since the time of the most-recent checkpoint are undone.
Figure 4-4 illustrates this step. (For more information about the contents and
function of the physical log, refer to page 2-152.)
Step 2: Find Checkpoint Record in Logical Log
The second step is to locate the address of the most-recent checkpoint record
in the logical log. The most-recent checkpoint record is guaranteed to be in
the logical log on disk.
All address information needed to locate the most-recent checkpoint record
in the logical log is contained in the active PAGE_CKPT page of the root
dbspace reserved pages.
Figure 4-4
Fast recovery,
step 1
Disk B
Fast Recovery: Step 1
Write “before-images” from the physical log back to disk, returning the data to
its state as of the most-recent checkpoint.
Disk A
Tblspace
Physical log


















