100 Storage Management with DB2 for OS/390
site. XRC externalizes a timestamp of the recovered system so that manual
recovery is possible from a specified time. The time lag between the primary and
the secondary sites can be minimized by performance tuning actions.
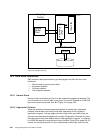
Figure 31. XRC Data Flow
9.5.5 Compression
Host compression techniques are commonly used to reduce the amount of
auxiliary storage required. As a general result, not only is storage space saved,
but also disk I/O; the data occupies less space; and fewer operations are required
to access and transfer the data on channels and networks. The cost is extra CPU
cycles needed at the host to compress the data before destaging to storage
servers and to decompress the data after it has been retrieved.
DB2 uses host compression and keeps the data compressed in the buffer pools
as well, effectively increasing their size, and decompressing only the rows
needed by the application programs. DB2 provides utilities that estimate the
compression values for your data, and therefore can help when evaluating the
trade off between DASD savings and CPU overhead.
Some disk storage servers, like RVA, store the user data in compressed form. In
such cases compression and decompression are independent of the host. So the
question arises about the usability of both levels of compression. Are they
compatible?
The answer is yes:
both can be used! Obviously, when you use both, the
effectiveness of the compression ratio between host data and stored data will be
considerably less than the 3.6 general value for traditional data, probably in the
range between 1.5 and 2.5, but still greater than 1. The RVA also implements
compaction and replaces the traditional device control information (such as gaps
and headers) with other techniques. In general, when capacity planning for large
storage occupancy, and the real amount of compressed data is not well defined,
consider some preliminary analysis of your RVA solution. There are tools
available to the IBM storage specialists in order to determine the specific
compression ratio by sampling the data of a given environment.
Please refer to
IBM RAMAC Virtual Array, SG24-4951, and to DB2 for OS/390
and Data Compression
, SG24-5261, for details on RVA and DB2 compression.
1. Write data to cache and NVS on primary
2. 3990 sidefile entry created
3. Device End - write complete
4. SDM reads sidefile using a utility address
5. SDM forms Consistency Group
- SDM optimizes secondary update process
6. SDM writes Consistency Group to journal
7. SDM updates Consistency Group on secondary devices
8. State data sets updated
1
3
4
6
7
8
5
2