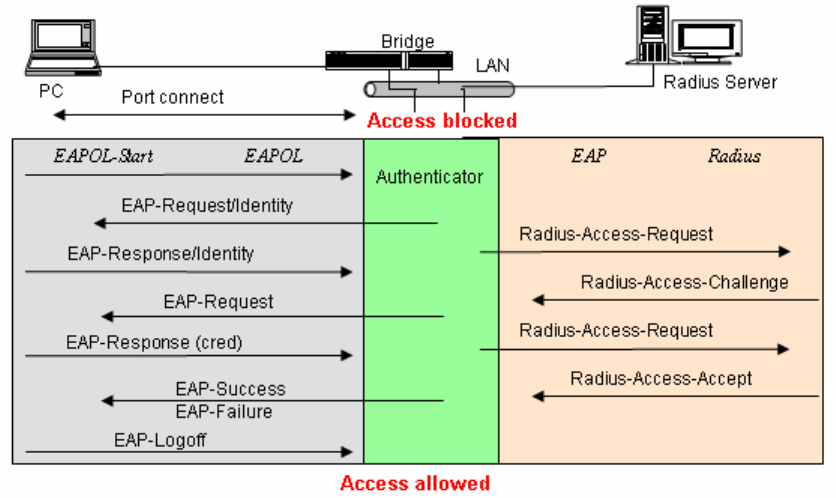
The figure as above shows the procedure of 802.1x authentication. There are steps for the login based on
802.1x port access control management. The protocol used in the right side is EAPOL and the left side is EAP.
1. At the initial stage, the supplicant A is unauthenticated and a port on switch acting as an
authenticator is in unauthorized state. So the access is blocked in this stage.
2. Initiating a session. Either authenticator or supplicant can initiate the message exchange. If
supplicant initiates the process, it sends EAPOL-start packet to the authenticator PAE and
authenticator will immediately respond EAP-Request/Identity packet.
3. The authenticator always periodically sends EAP-Request/Identity to the supplicant for requesting
the identity it wants to be authenticated.
4. If the authenticator doesn’t send EAP-Request/Identity, the supplicant will initiate EAPOL-Start the
process by sending to the authenticator.
5. And next, the Supplicant replies an EAP-Response/Identity to the authenticator. The authenticator
will embed the user ID into Radius-Access-Request command and send it to the authentication
server for confirming its identity.
6. After receiving the Radius-Access-Request, the authentication server sends
Radius-Access-Challenge to the supplicant for asking for inputting user password via the
authenticator PAE.
7. The supplicant will convert user password into the credential information, perhaps, in MD5 format
and replies an EAP-Response with this credential information as well as the specified
authentication algorithm (MD5 or OTP) to Authentication server via the authenticator PAE. As per
the value of the type field in message PDU, the authentication server knows which algorithm
should be applied to authenticate the credential information, EAP-MD5 (Message Digest 5) or
EAP-OTP (One Time Password) or other else algorithm.
8. If user ID and password is correct, the authentication server will send a Radius-Access-Accept to
the authenticator. If not correct, the authentication server will send a Radius-Access-Reject.
9. When the authenticator PAE receives a Radius-Access-Accept, it will send an EAP-Success to the
supplicant. At this time, the supplicant is authorized and the port connected to the supplicant and
under 802.1x control is in the authorized state. The supplicant and other devices connected to this
port can access the network. If the authenticator receives a Radius-Access-Reject, it will send an
EAP-Failure to the supplicant. This means the supplicant is failed to authenticate. The port it
46


















