Page 15
crystal where it is aligned as the image requires and reflected back out. If the
SXRD pixel has rotated the light, it then is not aligned with the post-PBS
polarization and is allowed to pass. If the incoming light has not been rotated,
then it is blocked by the post-PBS and reflected back into the source light path.
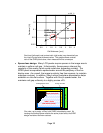
Photomicrograph of the SXRD panel silicon backplane in cross section.
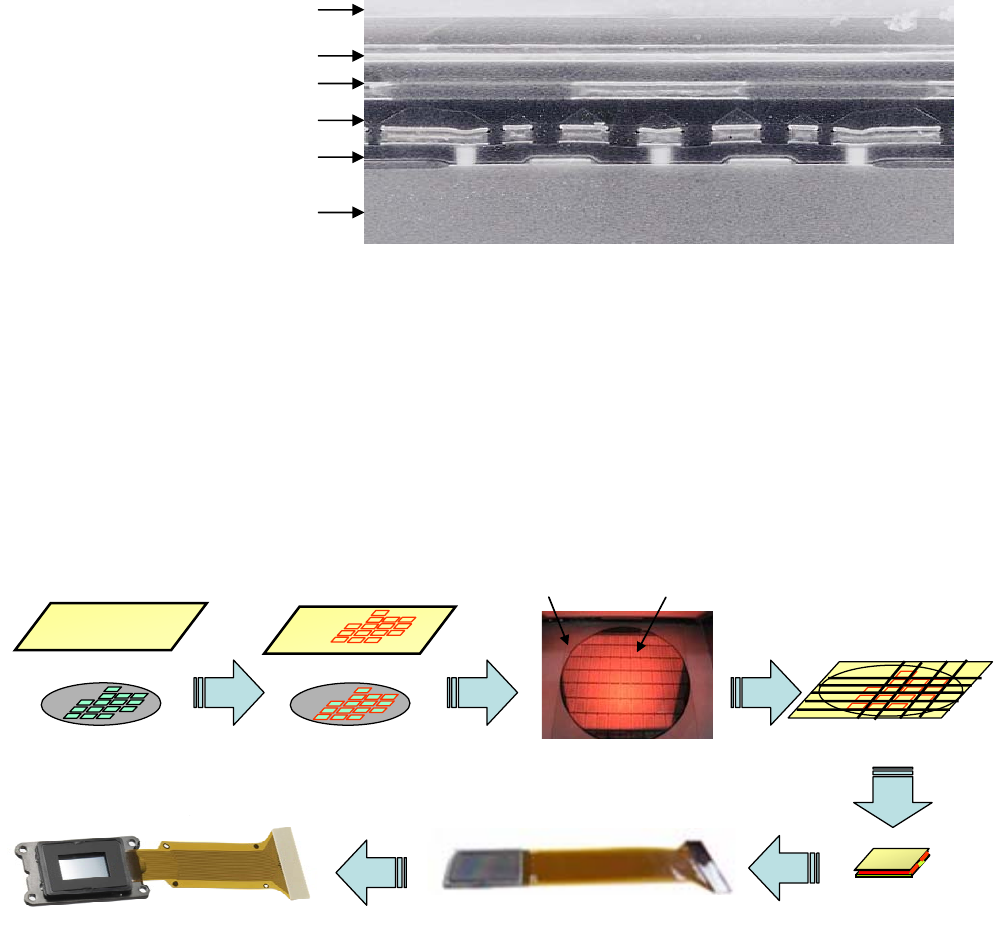
SXRD panel production
Unlike conventional LCoS panels, which are notoriously difficult to
manufacture, the SXRD panel uses a production process that Sony has
perfected in the company’s own, dedicated manufacturing facilities. This has
enabled Sony to bring SXRD technology smoothly into production, while taking
advantage of its many benefits.
Inorganic Alignment
Layer
IMITO glass
Si backplane
Print Sealing &
Common Electrode
Singlation
LC fill & Seal
Electrode Attachment
Packaging
IMITO glass
Si backplane
Assembly
Sony assembles the IMITO glass and silicon backplane prior to cutting
the wafer into individual panels (singlation). In this way, Sony achieves
three key features: a narrow cell gap, dust-free process and no LC gap
spacers in the image area.
Silicon Substrate
Polysilicon Process
1
st
Aluminum Process
2
nd
Aluminum Process
4
th
Aluminum Process
3
rd
Aluminum Process