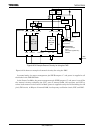
TMP92CZ26A
92CZ26A-631
(d) Sign mode
Both multiply-accumulate and multiply-subtract operations can be executed in unsigned
or signed mode.
In signed mode, the MACMA, MACMB, and MACOR registers become signed registers,
and the most significant bit is treated as the sign bit and the data set in each register is
treated as a two’s complement value.
Table 3.26.1 shows the range of values that can be
represented in each sign mode.
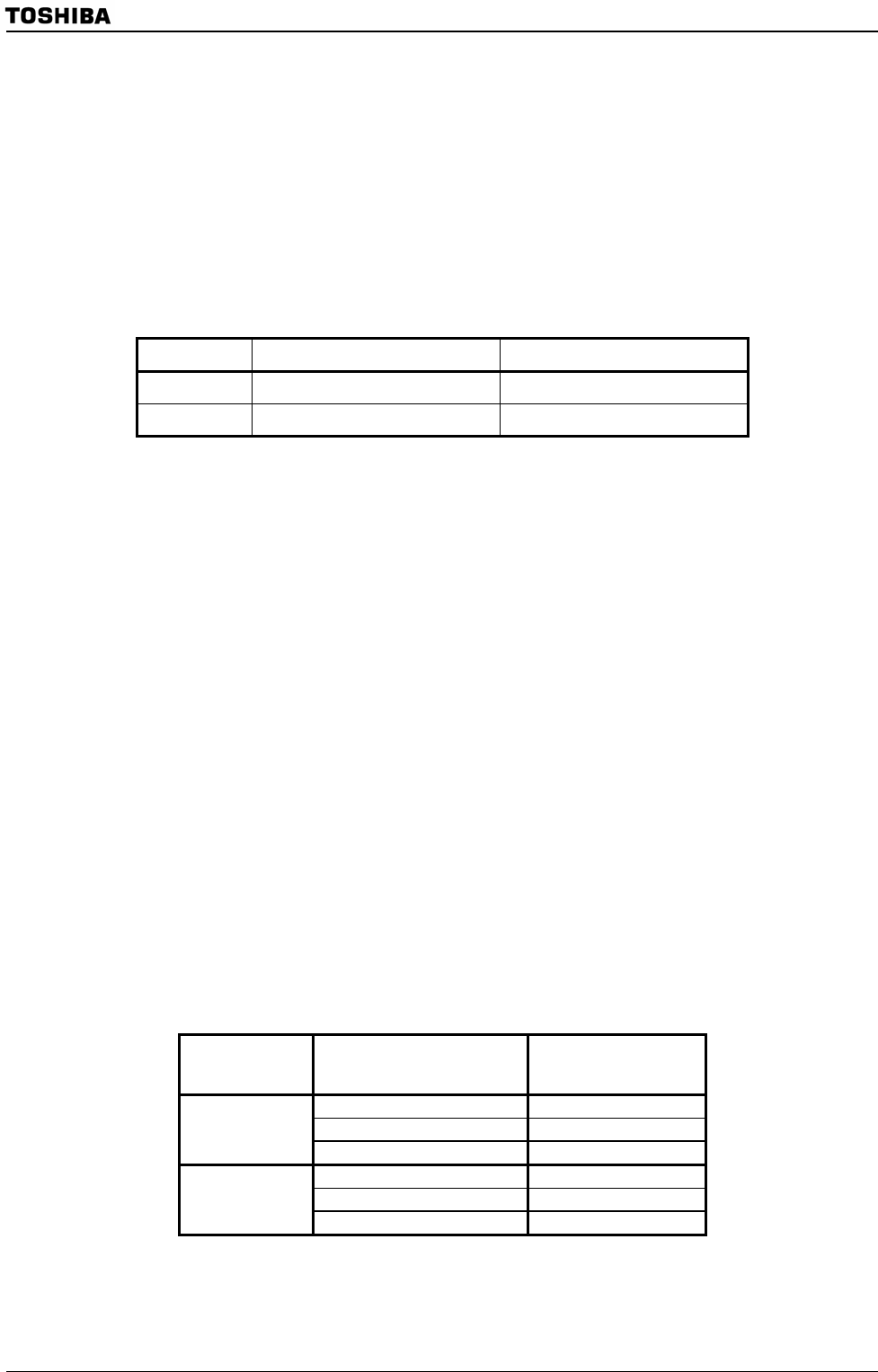
Table 3.26.1 Data Range in Unsigned/Signed Mode
MACMA, MACMB Registers MACOR Register
Unsigned 0 ∼ 2
32
−1 0 ∼ 2
64
−1
Signed −2
31
∼ +2
31
-1 −2
63
∼ +2
63
−1
Use signed mode when the values to be set in the MACMA and MACMB registers are
signed (two’s complement) data. Even in unsigned mode it is possible to set signed (two’s
complement) data in the MACOR register to perform additions and subtractions in signed
mode.
(2) Calculation start trigger
As a trigger to start calculation, writing to the MACMA, MACMB or MACOR register or
soft start (MACCR<MOPST>=1) can be selected in MACCR<MSTTG2:0>.
(3) Overflow flag
When an overflow occurs in the calculation result (see
Table 3.26.2), MACCR<MOVF> is set
to “1”. Once an overflow occurs, MACCR<MOVF> is held at “1” regardless of subsequent
calculation results. Since the overflow flag is not automatically cleared by a read operation, it
is necessary to write “0” to clear this flag.
Table 3.26.2 Overflow Definitions
Sign Mode
Calculation Result
(MACOR register value)
MACCR<MOVF>
MACOR > 2
64
−1 1
0 ≤ MACOR ≤ 2
64
−1 0
Signed
MACOR < 0 1
MACOR > 2
63
−1 1
−2
63
≤ MACOR ≤2
63
−1 0
Unsigned
MACOR < −2
63
1