Alcatel-Lucent 7705 SAR | Data Sheet2
The ASAP adapter card supports ATM,
inverse multiplexing over ATM (IMA),
TDM and MLPPP. The Ethernet adapter
card has six ports of auto-sensing 10/100
Base-T ports plus two further ports
supporting 10/100/1000 Base TX with
small form factor pluggable (SFPs) optics.
Each slot is connected to the switching
fabric on the CSM via a 1 Gb/s link to host
existing and future interface types.
Service aggregation
and networking
To provide the most efficient transport
solution, the Alcatel-Lucent 7705 SAR
employs pseudowire encapsulation
(PWE3) methods to map services end
to end. The use of pseudowires ensures
that the key attributes of the service
are maintained, while using a cost-
effective packet environment to
aggregate services.
The Alcatel-Lucent 7705 SAR supports
RFC 5086 — Structure-Aware Time
Division Multiplexed (TDM) Circuit
Emulation Service over Packet Switched
Network (CESoPSN) for the encap su-
lation and transport of TDM traffic,
for example, 2G TDM services. The use
of circuit emulation service (CES) ensures
that only the active timeslots are
transported, keeping bandwidth usage
to a minimum. The Alcatel-Lucent 7705
SAR also supports RFC 4717 — Encapsu-
lation Methods for Transport of
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
over MPLS Networks (also known as
draft-ietf-pwe3-atm-encap). The
Alcatel-Lucent 7705 SAR supports N:1
cell mode for transport of ATM-based
services. Multiple access ATM ports are
bundled together to attain higher
speeds using IMA. The IMA protocol
is terminated on the Alcatel-Lucent
7705 SAR and only the cells containing
user data belonging to a virtual
circuit/virtual path (VC/VP) structure
are transported.
In addition, the Alcatel-Lucent 7705
SAR supports RFC 4448 — Encapsu-
lation Methods for Transport of
Ethernet over MPLS Networks, which
specifies how Ethernet pseudowires
can be used to transport Ethernet
traffic across the packet network. To
offer greater scalability, all the traffic
out of an Ethernet port can be carried
over a single Ethernet pseudowire or,
alternatively, a pseudowire can be
created for each VLAN that is assigned
to a different service or end-customer.
When dynamic signaling is deployed,
the end-to-end pseudowire is estab-
lished using targeted label distribution
protocol (T-LDP) and the MPLS tunnel
via LDP. In addition to efficient
LDP-based dynamic signaling, static
provisioning of both the MPLS tunnel
and the pseudowire is also supported.
Quality of service and
traffic management
It is critical to maintain the end-to-end
quality of service (QoS) for packet traffic.
Not all types of traffic have the same
set of requirements. Voice traffic in
particular requires low latency and
jitter (latency variation) and also low
loss, whereas data traffic often has
less stringent delay requirements but
may be very sensitive to loss, as packet
loss can seriously constrain applica-
tion throughput. To offer the req-
uired treatment throughout the
network, traffic flows with different
require ments are identified at the
access and marked in-line with the
appropriate QoS metrics. Traffic
classification and marking is carried
out based on the following:
Classification (Layer 1/Layer 2/Layer
2.5 and/or Layer 3 header):
• Timeslot/port
• Ethernetport/VLAN
• ATMservicecategory
(CBR/rt-VBR/nrt-VBR/UBR)
• ATMVC
• Ethernet802.1p/VLAN
• IPDSCP/MPLSEXP
Marking:
• Layer2(802.1p)
• Layer2.5(EXP)bothfortunnel
and PWE3
• Layer3(DiffServ)
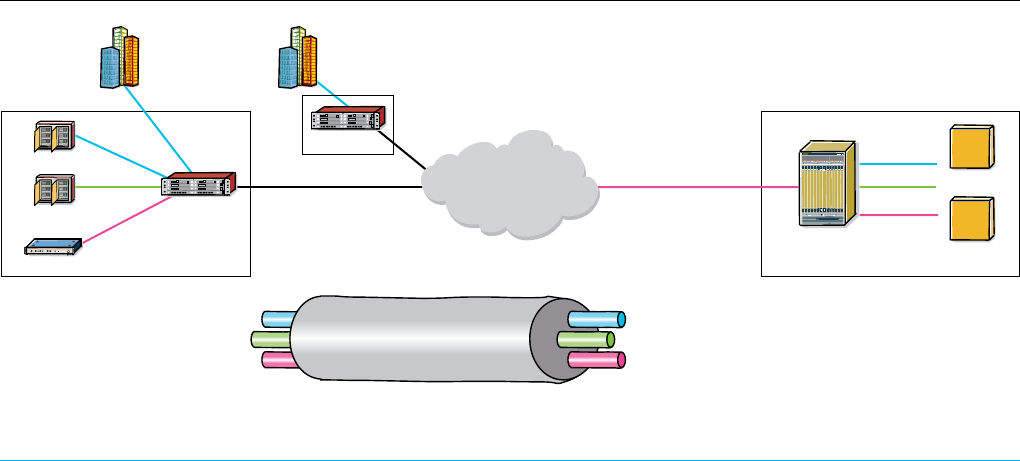
Figure 1. Low-cost, high-quality backhaul using MPLS pseudowires
BSC
RNC
Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet, MLPPPEthernet, MLPPP
ATM
ATM
TDM
TDM
MPLS Pseudowires Allow Convergence and Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation
Over Multiple Media, Enabling Low Cost Backhaul
Ethernet Pseudowire
ATM Pseudowire
TDM Pseudowire
MPLS Tunnel
PSN/Metro Ethernet/
SONET/SDH
Cell Site MTSO
Telemetry
BTS
Node B
7705
SAR
7710/7750 SR,
7670 RSP
7705 SAR








