PCE-N10 WLAN Card User Manual
17
ASUS WLAN Card
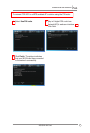
Cong - Encryption
The Encryption page allows you to set
up the encryption settings for your WLAN
card. For data condentiality in a wireless
environment, IEEE 802.11 species a Wired
Equivalent Privacy (WEP) algorithm to
offer transmission privacy similar to wired
network. WEP uses keys to encrypt data
packets sent and decrypt data packets
received. The encryption process can
scramble frame bits to avoid disclosure to others. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is
an improved security system for 802.11 that encrypts data sent over radio waves.
WPA is developed to overcome the weakness of the WEP protocol.
Network Authentication -
Set up authentication for your WLAN card. Options are:
Open -
Sets the network operating in the Open System mode that disables
authentication protection for the network or use the WEP encryption for the
network.
Shared -
Sets the network operating in the Shared Key mode that uses the
WEP encryption for your network.
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK -
Use the WPA Pre-Shared Key/WPA2 Pre-Shared Key
in the Infrastructure mode for authentication.
WPA/WPA2 -
Enables the IEEE 802.1x authentication mode. This mode is for
environments with Remote Access Dial-in User Service (Radius). In a RADIUS
environment, various Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) are supported,
including PEAP, TLS/Smart Card, TTLS, and LEAP.
Data Encryption -
In the Open and Shared authentication modes, options are:
Disabled and WEP.
Disabled -
Disables the encryption protection for your WLAN card.
WEP -
Encrypts the data before it is transmitted over the air. You can
communicate with wireless devices that use the same WEP keys.
In the WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK authentication modes, options are: Temporal Key
Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
TKIP -
Dynamically generates unique keys to encrypt data packet.
AES -
Offers stronger protection and increases the complexity of wireless
encryption. It is a symmetric 128-bit block encryption method that works
simultaneously on multiple network layers.