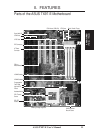
ASUS TX97-E User’s Manual 9
II. FEATURES
II. FEATURES
(TX97 Series)
Introduction to ASUS TX97 Series of motherboards
Performance:
• SDRAM Optimized Performance - ASUS TX97 series of motherboards sup-
port the new generation memory - Synchronous Dynamic Random Access
Memory (SDRAM) which increases the data transfer rate from 264MB/s max
using EDO memory to 528MB/s max.
• Double the IDE Transfer Speed - ASUS TX97 series of motherboards with
Intel 430TX PCIset improves IDE transfer rate using Bus Master UltraDMA/33
IDE which can handle data transfer up to 33MB/s. The best of all is that this
new technology is compatible with existing ATA-2 IDE specs so there is no
need to upgrade current hard drives or cables.
• Concurrent PCI - Concurrent PCI allows multiple PCI transfers from PCI master
busses to memory to CPU.
• ACPI Ready - ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) is also
implemented on all ASUS 430TX series of motherboards. ACPI provide more
Energy Saving Features for the future operating systems (OS) supporting OS
Direct Power Management (OSPM) functionality. With these features imple-
mented in the OS, PCs can be ready around the clock everyday, yet satisfy all
the energy saving standards. To fully utilize the benefits of ACPI, an ACPI-
supported OS such as in the next release of Windows 95 must be used.
• PC ’97 Compliant - Both the BIOS and hardware levels of ASUS TX97 series
of motherboards meet PC ’97 compliancy. The new PC 97 requirements for
systems and components are based on the following high-level goals: Support
for Plug and Play compatibility and power management for configuring and
managing all system components, and 32-bit device drivers and installation pro-
cedures for both Windows 95 and Windows NT.
Intelligence:
• Fan Status Monitoring and Alarm - To prevent system overheat and system
damage, the CPU fan and system fans are monitored for RPM and failure. Each
fan can be set for its normal RPM range and alarm thresholds.
• Temperature Monitoring and Alert - To prevent system overheat and system
damage, there is a heat sensor under the CPU and on the motherboard itself to
monitor CPU and system temperature to make sure the system is operating at a
safe heat level to avoid any failures triggered by extremely high temperature.