1-3
Cisco Aironet 350 Series Bridge Software Configuration Guide
OL-1410-07
Chapter 1 Overview
Management Options
–
The client generates a double encrypted session key and sends it to the access point along with
the chosen cipher specification.
–
The access point authenticates the client based on a user ID and password when the user
manager feature is enabled.
–
If authentication is successful, all management traffic between the client and access point is
encrypted using the session key.
Management Options
You can use the bridge management system through the following interfaces:
• A web-browser interface
• A command-line interface (CLI)
• Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
The bridge’s management system pages are organized the same way for the web- browser interface and
the CLI. The examples in this manual are all taken from the web-browser interface. Chapter 2, “Using
the Management Interfaces” provides a detailed description of each management option.
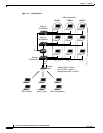
Roaming Client Devices
If you have more than one bridge or access point in your wireless LAN, wireless client devices can roam
seamlessly from one bridge or access point to another. The roaming functionality is based on signal
quality, not proximity. When a client’s signal quality drops, it roams to another bridge or access point.
Wireless LAN users are sometimes concerned when a client device stays associated to a distant bridge
or access point instead of roaming to a closer bridge or access point. However, if a client’s signal to a
distant bridge or access point remains strong, the client will not roam to a closer bridge or access point.
If client devices checked constantly for closer bridges and access points, the extra radio traffic would
slow throughput on the wireless LAN.
Quality of Service Support
The bridge now supports Cisco’s QoS, primarily in the area of wireless VoIP telephones from
Spectralink and Symbol Technologies Corporation. The bridge also provides priority classification,
prioritized queueing, and prioritized channel access for other downlink IEEE 802.11 traffic such as
streaming audio or video traffic.
With this software release, the bridge does not include any QoS enhancements in Cisco IEEE 802.11
client software.
What is QoS?
QoS refers to the ability of a network to provide improved service to selected network traffic over various
underlying technologies including Ethernet and wireless LANs. In particular, QoS features provide
improved and more predictable network service by providing the following services:
• Improving loss characteristics