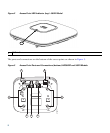
13
e. CAPWAP UDP ports must not be blocked in the network.
f. The access point must be able to find the IP address of the controller. This can be
accomplished using DHCP, DNS, or IP subnet broadcast. This guide describes the DHCP
method to convey the controller IP address. For other methods, refer to the product
documentation. See also the “Using DHCP Option 43” section on page 18 for more
information.
Step 2 Apply power to the access point:
a. The access point is 802.3af (15.4 W) compliant and can be powered by any of the following
802.3af compliant devices:
–
2106 controller
–
WS-C3550, WS-C3560, and WS-C3750 switches
–
C1880 switch
–
2600, 2610, 2611, 2621, 2650, and 2651 multiservice platforms
–
2610XM, 2611XM, 2621XM, 2650XM, 2651XM, and 2691 multiservice platforms
–
2811, 2821, and 2851 integrated services routers
–
3620, 3631-telco, 3640, and 3660 multiservice platforms
–
3725 and 3745 multiservice access routers
–
3825 and 3845 integrated services routers
The recommended external power supply for the access point is the Cisco AIR-PWR-B
power supply. The access point can also be powered by the following optional external
power sources:
–
1250 series access point power injector (AIR-PWRINJ4)
–
Any 802.3af compliant power injector
Note The 3602 series access point requires a Gigibit Ethernet link to prevent the Ethernet
port from becoming a bottleneck for traffic because wireless traffic speeds exceed
transmit speeds of a 10/100 Ethernet port.
b. As the access point attempts to connect to the controller, the LEDs cycle through a green, red,
and amber sequence, which can take up to 5 minutes.
Note If the access point remains in this mode for more than five minutes, the access point is
unable to find the Master Cisco wireless LAN controller. Check the connection between
the access point and the Cisco wireless LAN controller and be sure that they are on the
same subnet.