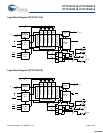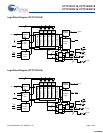
CY7C1241V18, CY7C1256V18
CY7C1243V18, CY7C1245V18
Document Number: 001-06365 Rev. *D Page 6 of 28
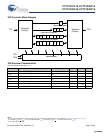
Pin Definitions
Pin Name IO Pin Description
D
[x:0]
Input-
Synchronous
Data Input Signals. Sampled on the rising edge of K and K
clocks during valid write operations.
CY7C1241V18 − D
[7:0]
CY7C1256V18 − D
[8:0]
CY7C1243V18 − D
[17:0]
CY7C1245V18 − D
[35:0]
WPS Input-
Synchronous
Write Port Select, Active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of the K clock. When asserted
active, a Write operation is initiated. Deasserting deselects the write port. Deselecting the write
port causes D
[x:0]
to be ignored.
NWS
0
,
NWS
1
,
Input-
Synchronous
Nibble Write Select 0, 1, Active LOW (CY7C1241V18 Only). Sampled on the rising edge of
the K and K clocks when write operations are active. Used to select which nibble is written into
the device during the current portion of the write operations. NWS
0
controls D
[3:0]
and NWS
1
controls D
[7:4]
.
All the nibble Write Selects are sampled on the same edge as the data. The corresponding nibble
of data is ignored by deselecting a nibble write select and is not written into the device.
BWS
0
, BWS
1
,
BWS
2
, BWS
3
Input-
Synchronous
Byte Write Select 0, 1, 2, and 3, Active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of the K and K
clocks
during write operations. Selects which byte is written into the device during the current portion
of the write operations. Bytes not written remain unaltered.
CY7C1256V18 − BWS
0
controls D
[8:0]
CY7C1243V18 − BWS
0
controls D
[8:0]
and BWS
1
controls D
[17:9].
CY7C1245V18 − BWS
0
controls D
[8:0]
, BWS
1
controls D
[17:9]
, BWS
2
controls D
[26:18]
, and BWS
3
controls D
[35:27].
All the Byte Write Selects are sampled on the same edge as the data. Deselecting a Byte Write
Select ignores the corresponding byte of data and not written into the device.
A Input-
Synchronous
Address Inputs. Sampled on the rising edge of the K clock during active read and write opera-
tions. These address inputs are multiplexed for both read and write operations. Internally, the
device is organized as 4M x 8 (4 arrays each of 1M x 8) for CY7C1241V18, 4M x 9 (4 arrays
each of 1M x 9) for CY7C1256V18, 2M x 18 (4 arrays each of 512K x 18) for CY7C1243V18
and 1M x 36 (4 arrays each of 256K x 36) for CY7C1245V18. Therefore, only 20 address inputs
are needed to access the entire memory array of CY7C1241V18 and CY7C1256V18, 19 address
inputs for CY7C1243V18, and 18 address inputs for CY7C1245V18. These inputs are ignored
when the appropriate port is deselected.
Q
[x:0]
Outputs-
Synchronous
Data Output Signals. These pins drive out the requested data during a read operation. Valid
data is driven out on the rising edge of both the K and K
clocks during read operations. When
the read port is deselected, Q
[x:0]
are automatically tri-stated.
CY7C1241V18 − Q
[7:0]
CY7C1256V18 − Q
[8:0]
CY7C1243V18 − Q
[17:0]
CY7C1245V18 − Q
[35:0]
RPS Input-
Synchronous
Read Port Select, Active LOW. Sampled on the rising edge of Positive Input Clock (K). When
active, a read operation is initiated. Deasserting causes the read port to be deselected. When
deselected, the pending access is allowed to complete and the output drivers are automatically
tri-stated following the next rising edge of the K clock. Each read access consists of a burst of
four sequential transfers.
QVLD Valid output
indicator
Valid Output Indicator. The Q Valid indicates valid output data. QVLD is edge aligned with CQ
and CQ
.
K Input-
Clock
Positive Input Clock Input. The rising edge of K captures synchronous inputs to the device
and drives out data through Q
[x:0]
when in single clock mode. All accesses are initiated on the
rising edge of K.
K
Input-
Clock
Negative Input Clock Input. K captures synchronous inputs being presented to the device and
drives out data through Q
[x:0]
when in single clock mode.
[+] Feedback [+] Feedback