PRELIMINARY
CY7C2561KV18, CY7C2576KV18
CY7C2563KV18, CY7C2565KV18
Document Number: 001-15887 Rev. *E Page 9 of 29
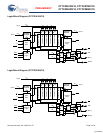
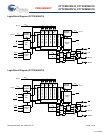
Read access and write access must be scheduled such that one
transaction is initiated on any clock cycle. If both ports are
selected on the same K clock rise, the arbitration depends on the
previous state of the SRAM. If both ports are deselected, the
read port takes priority. If a read was initiated on the previous
cycle, the write port takes priority (as read operations can not be
initiated on consecutive cycles). If a write was initiated on the
previous cycle, the read port takes priority (as write operations
can not be initiated on consecutive cycles). Therefore, asserting
both port selects active from a deselected state results in alter-
nating read or write operations being initiated, with the first
access being a read.
Depth Expansion
The CY7C2563KV18 has a port select input for each port. This
enables for easy depth expansion. Both port selects are sampled
on the rising edge of the positive input clock only (K). Each port
select input can deselect the specified port. Deselecting a port
does not affect the other port. All pending transactions (read and
write) are completed before the device is deselected.
Programmable Impedance
An external resistor, RQ, must be connected between the ZQ pin
on the SRAM and V
SS
to allow the SRAM to adjust its output
driver impedance. The value of RQ must be 5X the value of the
intended line impedance driven by the SRAM, the allowable
range of RQ to guarantee impedance matching with a tolerance
of ±15% is between 175Ω and 350Ω
, with V
DDQ
=1.5V. The
output impedance is adjusted every 1024 cycles upon power up
to account for drifts in supply voltage and temperature.
Echo Clocks
Echo clocks are provided on the QDR-II+ to simplify data capture
on high-speed systems. Two echo clocks are generated by the
QDR-II+. CQ is referenced with respect to K and CQ is refer-
enced with respect to K
. These are free-running clocks and are
synchronized to the input clock of the QDR-II+. The timing for the
echo clocks is shown in the Switching Characteristics on page
24.
Valid Data Indicator (QVLD)
QVLD is provided on the QDR-II+ to simplify data capture on high
speed systems. The QVLD is generated by the QDR-II+ device
along with data output. This signal is also edge-aligned with the
echo clock and follows the timing of any data pin. This signal is
asserted half a cycle before valid data arrives.
On-Die Termination (ODT)
These devices have an On-Die Termination feature for Data
inputs (D
[x:0]
), Byte Write Selects (BWS
[x:0]
), and Input Clocks (K
and K
). The termination resistors are integrated within the chip.
The ODT range selection is enabled through ball R6 (ODT pin).
The ODT termination tracks value of RQ where RQ is the resistor
tied to the ZQ pin. ODT range selection is made during power up
initialization. A LOW on this pin selects a low range that follows
RQ/3.33 for 175Ω <
RQ < 350Ω (where RQ is the resistor tied to
ZQ pin). A HIGH on this pin selects a high range that follows
RQ/1.66 for 175Ω <
RQ < 250Ω (where RQ is the resistor tied to
ZQ pin). When left floating, a high range termination value is
selected by default. For a detailed description on the ODT imple-
mentation, refer to the application note, On-Die Termination for
QDRII+/DDRII+ SRAMs.
PLL
These chips use a PLL that is designed to function between 120
MHz and the specified maximum clock frequency. During power
up, when the DOFF
is tied HIGH, the PLL is locked after 20 μs
of stable clock. The PLL can also be reset by slowing or stopping
the input clocks K and K for a minimum of 30 ns. However, it is
not necessary to reset the PLL to lock to the desired frequency.
The PLL automatically locks 20 μs after a stable clock is
presented. The PLL may be disabled by applying ground to the
DOFF
pin. When the PLL is turned off, the device behaves in
QDR-I mode (with one cycle latency and a longer access time).
For information, refer to the application note, PLL Considerations
in QDRII/DDRII/QDRII+/DDRII+.
[+] Feedback