Dell
DELL PERC H700 and H800 Technical Guide 22
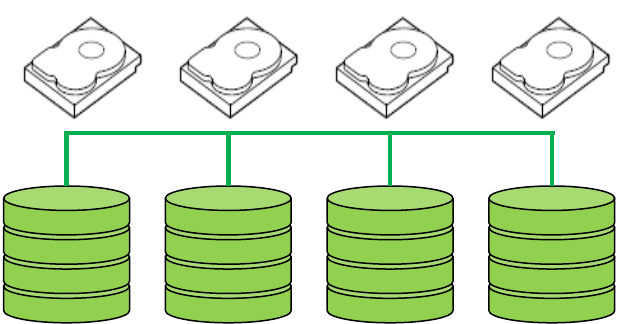
For example, a four-drive virtual disk may be configured with 16 stripes (four stripes of designated
space per drive). Stripes A, B, C and D are located on corresponding hard drives 0, 1, 2, and 3. Stripe
E, however, appears on a segment of drive 0 in a different location than stripe A; stripes F through H
appear accordingly on drives 1, 2 and 3. The remaining eight stripes are allocated in the same even
fashion across the drives.
RAID 0 provides improved performance because each drive in the virtual disk needs to handle only
part of a read or write request. However, because none of the data is mirrored or backed up on
parity drives, one drive failure makes the virtual disk inaccessible and the data is lost permanently.
Figure 4. Example of RAID 0
Advantages of RAID 0
I/O performance is greatly improved by spreading the I/O load across many channels and
drives (best performance is achieved when data is striped across multiple channels with only
one drive per channel)
No parity calculation overhead is involved
Very simple design
Easy to implement
Disadvantages of RAID 0
Not a "true" RAID because the failure of just one drive will result in all data in a virtual disk
being lost
Should not be used for critical data unless another form of data redundancy is deployed
5.3.2 RAID 1 (Mirroring)
RAID 1 is achieved through disk mirroring to ensure data reliability or a high degree of fault
tolerance. In a RAID 1 configuration, the RAID management software instructs the subsystem's
controller to store data redundantly across a number of the drives (mirrored set) in the virtual disk.
See Figure 5.
In other words, if a disk fails, the mirrored drive takes over and functions as the primary drive.
Drive 0
Drive 1
Drive 2
Drive 3
Data 1
Data 16
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4
Data 5
Data 6
Data 7
Data 8
Data 9
Data 10
Data 11
Data 12
Data 13
Data 14
Data 15


















