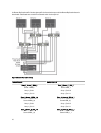
Switch Zoning Guidelines
The storage array imposes specific requirements that must be followed when setting up Fibre Channel switch zoning:
• If a Fibre Channel switch is used to connect your host server and storage array, it must be zoned. Un-zoned or
open switches cannot be used.
• WWN port zoning is recommended. While
hard zoning
(zoning by device ID) is supported, LUN masking uses the
WWN identifier. You can mix WWN and hard-zoned ports in the same zone.
• Multi-port HBAs are supported. Each port in a multiple-port HBA represents one initiator. Each initiator must be
connected to a single logical switch zone.
• No more than four paths (port-to-port segments) can be established from a single, physical host server to a
single RAID controller.
• A zone can contain multiple targets and span multiple storage arrays (single initiator can point to multiple
targets).
• If the Remote Replication premium feature is activated, a separate zone for each replication port is required.
Only data traffic related to Remote Replication can move through that zone. For more details and requirements
regarding Remote Replication, see the
Dell PowerVault MD3260/3260i/3660i/3660f/3060e Storage Arrays
Administrator's Guide
at support.dell.com/manuals.
Setting Up Zoning On The Fibre Channel Switch Hardware
Setting up zoning on Fibre Channel switches varies greatly between manufacturers. For detailed information on how to
set up zoning on your switch, see the manufacturer’s product documentation or technical support website.
Cabling The Storage Array
Cabling the storage array depends on a number of factors such as:
• Direct- or SAN-attached storage array
• Required level of redundancy or throughput
• Number of host servers connected to the storage array
• Type of HBAs (dual- or single-port) used in the host server(s)
• Remote Replication premium feature (if applicable)
The cabling diagrams shown here do not represent every supported cabling scenario but the concepts of redundancy
and switch logic can be used to build your own configuration.
Redundant And Non-Redundant Cabling
Non-redundant cabling configurations provide a single data path from a host server to the storage array. This type of
configuration is only recommended for non-critical data storage. A path failure from a failed or removed cable, failed
HBA, or failed or removed RAID controller module results in loss of host access to the storage array.
Redundant configurations establish separate data paths between the host server and storage array. Each path is
connected to separate RAID controller modules in the storage array. Redundancy protects the host server from losing
access to data in the event of a path failure since both RAID controller modules can independently access all the
physical disks in the storage array.
8