136 IPv6
• Allocated from part of the IPv6 unicast address space
• Not visible off the local link
• Not globally unique
Next hop addresses computed by routing protocols are usually link-local.
During a transition period, a global IPv6 Internet backbone may not be available. The solution of this is
to tunnel IPv6 packets inside IPv4 to reach remote IPv6 islands. When a packet is sent over such a link, it
is encapsulated in IPv4 in order to traverse an IPv4 network and has the IPv4 headers removed at the
other end of the tunnel.
CLI Example
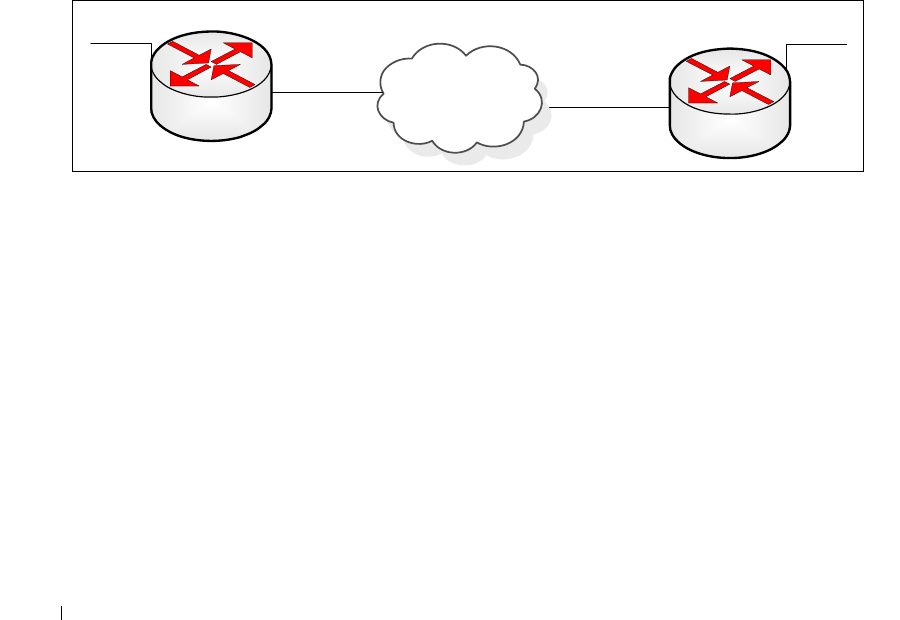
In Figure 6-1, two devices are connected as shown in the diagram. The VLAN 15 routing interface on
both devices connects to an IPv4 backbone network where OSPF is used as the dynamic routing protocol
to exchange IPv4 routes. OSPF allows device 1 and device 2 to learn routes to each other (from the
20.20.20.x network to the 10.10.10.x network and vice versa). The VLAN 2 routing interface on both
devices connects to the local IPv6 network. OSPFv3 is used to exchange IPv6 routes between the two
devices. The tunnel interface allows data to be transported between the two remote IPv6 networks over
the IPv4 network.
Figure 6-1. IPv6 Example
Device 1
console# config
ip routing
ipv6 unicast-routing
router ospf
router-id 1.1.1.1
exit
ipv6 router ospf
router-id 1.1.1.1
exit
interface vlan 15
routing
ip address 20.20.20.1 255.255.255.0
VLAN 2
VLAN 15
VLAN 2
VLAN 15
Network


















