7
8.2 Output Characteristics
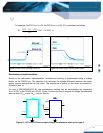
8.2.1 Line Regulation
Line Regulation Deviation is defined as the change in output voltage caused by varying the
input voltage over a specified range while the output load and temperature remain constant.
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the output power to the desired operating point.
3) Set the switch SW2 to the converter ON.
4) Adjust the input voltage across the converter’s input range (refer to specified range) while
monitoring DVM2.
5) Note the maximum +/- deviation of the output voltage over the full range of the input
operating voltage (please refer to the data sheet for the detailed specification).
8.2.2 Load Regulation
Load Regulation Deviation is defined as the change in output voltage caused by varying the
output load current over the specified range (no load to full load) while the input voltage and
temperature remain constant.
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the input voltage to the desired operating level while monitoring DVM2.
3) Set the switch SW2 to the converter ON.
4) Adjust the output load across the converter’s operating load range.
5) Note the maximum +/- deviation of the output voltage over the full range of the operating
load range (please refer to the data sheet for the detailed specification).
8.2.3 Output Ripple
Output Ripple is defined as the periodic AC component on the DC/DC converter’s output
voltage. The output ripple is measured in terms of peak to peak and RMS values, both done
with a specific bandwidth.
Test
1) Turn on the fan.
2) Set the switch SW2 to the converter ON.
3) Adjust the input voltage while monitoring DVM2 and set the output load to the full rated
load current.
4) Adjust channel 2 on the oscilloscope to be AC coupled at 4µS/Div and at 10mV/Div using
the 20 MHz bandwidth-limit option on the scope.
5) The output ripple of the DC/DC converter is measured at full load operating power.