RX
-
8581
SA
/
JE
/
NB
Page - 27 MQ372-02
10. Reference Data
[Finding the frequency stability]
1. Frequency and temperature characteristics can be
approximated using the following equations.
∆f
T
= α (θ
T
- θ
X
)
2
∆f
T
: Frequency deviation in any
temperature
α (1 / °C
2
)
: Coefficient of secondary temperature
(−0.035±0.005) × 10
-6
/ °C
2
θ
T
(°C) : Ultimate temperature (+25±5 °C)
θ
X
(°C)
: Any temperature
2. To determine overall clock accuracy, add the frequency
precision and voltage characteristics.
∆f/f
= ∆f/fo + ∆f
T
+ ∆f
V
∆f/f
: Clock accuracy (stable frequency) in any
temperature and voltage
∆f/fo
: Frequency precision
∆f
T
: Frequency deviation in any temperature
∆f
V
: Frequency deviation in any voltage
3. How to find the date difference
Date difference = ∆f/f × 86400 (seconds)
* For example: ∆f/f = 11.574 × 10
-6
is an error of
approximately 1 second/day.
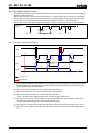
(1) Example of frequency and temperature characteristics
-150
-100
-50
0
-50 0 +50 +100
Temperature [
°
C]
Frequency
∆
f
T
×
10
-6
θ
T
= +25
°
C Typ.
α
= -0.035
×
10
-6
Typ.
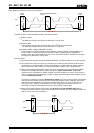
(2) Example of frequency and voltage characteristics
- 3
2
Frequency
∆
f
v
×
10
−
6
+ 3
0
3 4 5
Condition :
3 V as reference, Ta=+25 °C
Supply Voltage V
DD
[V]
(3) Current and voltage consumption characteristics
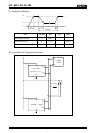
(3-1) Current consumption when non-accessed (i)
when FOUT=OFF
2
Current consumption [
µ
A]
Supply Voltage V
DD
[V]
1.0
0.5
3 4 5
Condition :
Ta = +25
°
C
f
SCL
= 0 Hz
FOE = GND, /INT = V
DD
FOUT ; Output OFF
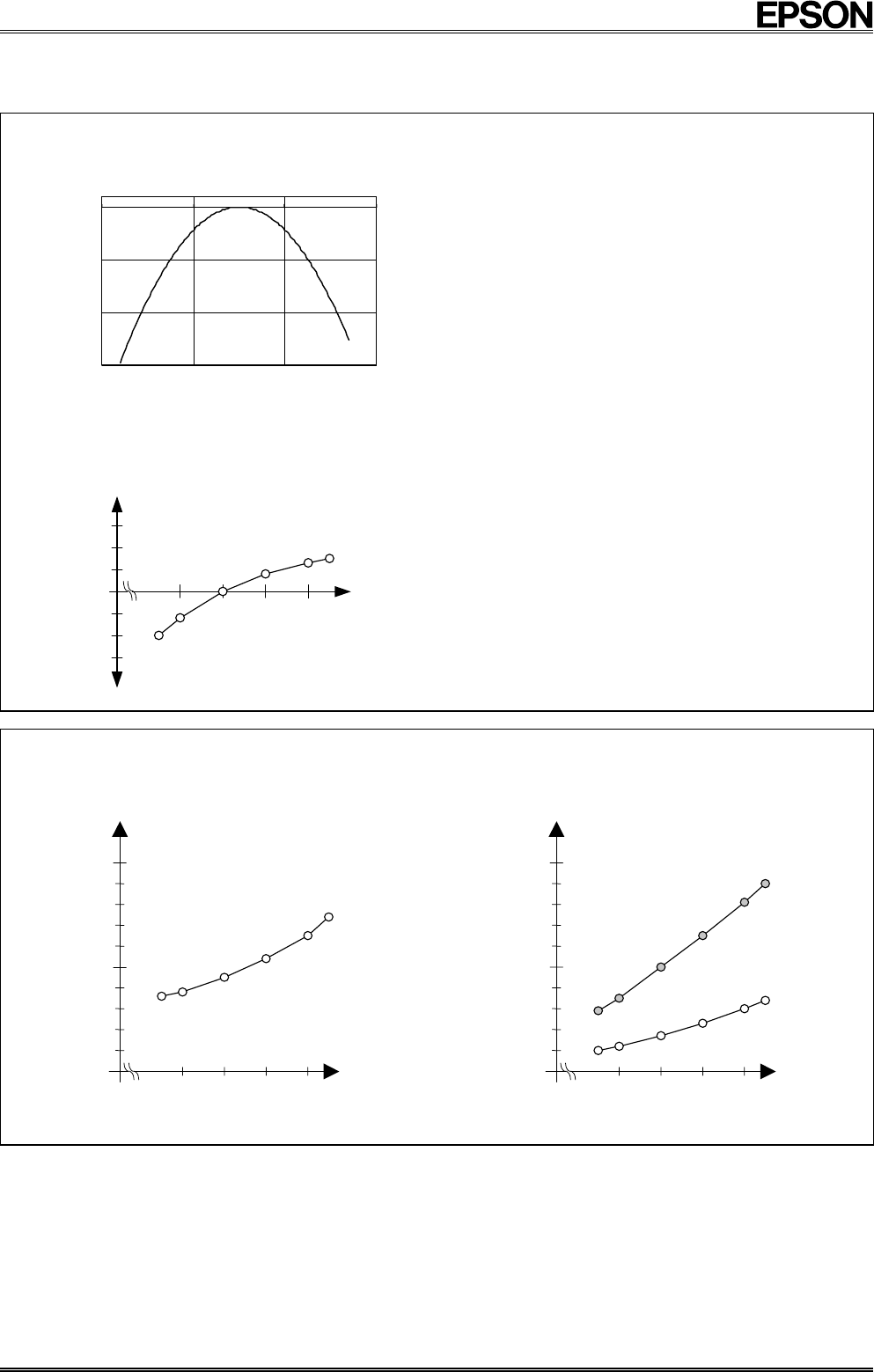
(3-2) Current consumption when non-accessed (ii)
when FOUT=32.768 kHz
2
10
5
3 4 5
CL=0 pF
Current consumption [
µ
A]
Condition :
Ta = +25
°
C
f
SCL
= 0 Hz
FOE, /INT = V
DD
FOUT ; 32.768 kHz output ON
Supply Voltage V
DD
[V]
CL=30 pF