C141-E064-03EN3 - 10
3.1.5 Format capacity
The size of the usable area for storing user data on the IDD (format capacity) varies according
to the logical data block or the size of the spare sector area. Table 3.4 lists examples of the
format capacity when the typical logical data block length and the default spare area are used.
The following is the general formula to calculate the format capacity.
[Number of sectors of each zone] = [number of sectors per track × number of tracks (heads) –
number of alternate spare sectors per cylinder] × [number of cylinders in the zone]
[Formatted capacity] = [total of sectors of all zones] – [number of sectors per track in last zone
× number of tracks (heads) × number of alternate cylinders] ÷ [number of physical sectors in
logical block] × [logical data block length]
The following formula must be used when the number of logical data blocks are specified with
the parameter in the MODE SELECT or MODE SELECT EXTENDED command.
[Format capacity] = [logical data block length] × [number of logical data blocks]
The logical data block length, the maximum logical block address, and the number of the
logical data blocks can be read out by a READ CAPACITY, MODE SENSE, or MODE
SENSE EXTENDED command after initializing the disk medium.
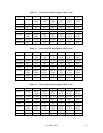
Table 3.4 Format capacity
Model Data heads Data block length User blocks Format capacity (GB)
MAE3182 series 8 35,700,480 18.2
MAE3091 series 4 17,826,240 9.1
MAF3364 series 19 512 71,161,520 36.4
MAG3182 series 10 35,694,860 18.2
MAG3091 series 5 17,827,698 9.1
Note:
Total number of spare sectors is calculated by adding the number of spare sectors in each
primary cylinder and the number of sectors in the alternate cylinders.