RAID Explained
RAID - Redundant Array of Independent Disks
RAID technology manages multiple disk drives to enhance I/O performance and provide redundncy in
order to withstand the failure of any individual member, without loss of data.
SATARaid provides two RAID Set types, Striped (RAID 0) and Mirrored (RAID 1).
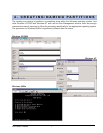
Disk Striping (RAID 0)
Striping is a performance-oriented, non-redundant data mapping technique. While Striping is discussed
as a RAID Set type, it is actually does not provide fault tolerance. With modern SATA and ATA bus mas-
tering technology, multiple I/O operations can be
done in parallel, enhancing performance. Striping
arrays use multiple disks to form a larger virtual disk.
This figure shows a stripe set using three disks with
stripe one written to disk one, stripe two to disk two,
and so forth.
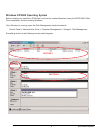
Disk Mirroring (RAID 1)
Disk mirroring creates an identical twin for a selected disk by having the
data simultaneously written to two disks. This redundancy provides instan-
taneous protection from a single disk failure. If a read failure occurs on one
drive, the system reads the data from the other drive.
Strip 2
Strip 5
Strip 8
Strip 11
Strip 0
Strip 3
Strip 6
Strip 9
Strip 1
Strip 4
Strip 7
Strip 10
Block 0
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Block 0
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
SATA RAID Function
2