General Information 15
Specifications
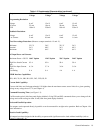
Table 1-2 lists the performance specifications for the HP 662xA power supplies. Performance specifications describe the
instrument's warranted performance. The service manual, Option 9l0, contains procedures for verifying the performance
specifications.
Table 1-3 lists the supplemental characteristics for the HP 662xA supplies. Supplemental characteristics are type-tested or
typical values, which are based on a product sample and, while representative, are not guaranteed.
Qualifying Conditions
All performance specifications apply over the full operating temperature range of the power supply (0 to 55°C) unless
otherwise specified. All regulation, accuracy, etc. specifications are plus or minus the values listed. All measurements are
made at the rear terminals of the supply with a resistive load and local sensing unless otherwise specified. Voltage
measurements are made from the + S to the - S terminals. Overvoltage measurements are made from the + V to the - V
terminals. + Current refers to the output acting as a current source while - Current refers to the output acting as a current
sink.
Definitions
Load effect: Maximum steady state change in the regulated output parameter due to a change in load resistance on the
output in question.
Source effect: Maximum steady state change in the regulated output parameter due to a change in the source voltage
within rated values. (Expressed as a percentage of setting plus a constant).
Cross regulation: Maximum steady state change in the regulated output parameter due to a change in load resistance on
any other output(s).
Programming accuracy: (Calibration temp ± 5°C) Maximum difference between the programmed value and the actual
output. (Expressed as a constant plus a percentage of the setting.)
Readback accuracy: (Calibration temp ± 5°C) Maximum error in reading back an output parameter. (Expressed as a
constant plus a percentage of the reading).
Output response time: Beginning at the time the power supply has finished processing a VSET command (change output
voltage), the maximum time for the output voltage to settle to within a settling band about the final value from any
specified operating point. This value must be added to the command processing time to obtain total programming time
(see Figure 1-3). Time constant is the maximum time required for the voltage to reach 63% of its final value.
Temperature coefficient: Maximum change in the regulated output parameter per °C change in ambient temperature
after a 30 minute warmup. Expressed in parts-per-million plus a constant per °C (plus a constant for readback
temperature coefficient).
Long Term Drift: Maximum change of regulated output voltage or current during an 8-hour period following a 30
minute warmup, with all influence and control quantities maintained constant. Expressed as a percentage of setting plus a
constant.
Short Term Drift: Maximum change of regulated output voltage or current within 30 minutes after a line and/or load
change. Expressed as a percentage of setting plus a constant.
Output Noise (PARD): PARD replaces the former term ripple and noise. PARD is the periodic and random deviation of
dc output voltage or current from its average value, over a specified bandwidth and with all influence and control
quantities maintained constant.