Storage planning considerations include:
• System and performance expectations
• Striping methods
• RAID levels
• Disk drive sizes and types
• Spare drives
• Array sizing (capacity)
NOTE:
For the minimum supported configuration, and other configuration information, see the QuickSpecs
for the disk enclosure.
System and performance expectations
To help determine the best way to configure your storage, rank the following three storage
characteristics in order of importance:
• Fault tolerance (high availability)
• I/O performance
• Storage efficiency
With priorities established, you can determine which striping method and RAID level to use; some
configuration methods offer greater fault tolerance, while other configuration methods offer better I/O
performance or storage efficiency.
Striping methods
There are two methods for configuring the physical layout of the disk arrays:
• Vertical striping—the RAID array uses one physical drive from each disk enclosure.
• Horizontal striping—the RAID array uses multiple drives contained within one or more disk enclos-
ures.
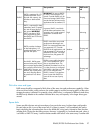
RAID levels
Controllers use RAID technology to group multiple disk drives together in larger logical units (LUNs).
Key RAID methods include the use of data striping, data mirroring, and parity error checking. Data
striping improves speed by performing virtual disk I/O with an entire group of physical disks at the
same time. Mirroring provides data redundancy by storing data and a copy of the data. Parity error
checking provides automatic detection and correction if corruption of a physical disk occurs.
Depending on the host environment, the following RAID levels are supported with this disk enclosure:
RAID0, RAID1, RAID5 and RAID6 with ADG. Each level uses a different combination of RAID methods
that impact data redundancy, the amount of physical disk space used, and I/O speed. After you
create a LUN, you cannot change the RAID level.
The following table compares the different RAID levels.
Installation26