Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
7
times the maximum throughput of a 133MHz PCI-X adapter
3
. (A x1 adapter offers throughput
similar to a 66MHz PCI-X slot.)
Because the SAS, ServeRAID-MR10k, dual Gigabit Ethernet, and systems management
controllers are integrated onto the system board, the seven adapter slots are all available, which
offers you a wide degree of latitude in expansion options.
(Even though the HP DL580G5 has eleven total slots, they offer lower throughput, providing no
more aggregate bandwidth than the seven slots of the eX4 servers.)
Dual Gigabit Ethernet Controller
The eX4 systems include one integrated dual-port Broadcom 5709C Gigabit Ethernet
controller, with TOE (TCP Offload Engine) acceleration support (available 1Q/08), as well as
load-balancing and failover capabilities between the two ports.
TOE support helps improve overall system performance by offloading TCP/IP protocol
processing from the system microprocessor to the onboard Ethernet TOE processor. iSCSI
support works similarly for iSCSI workloads.
The controller also supports highly secure remote power management using IPMI 2.0, plus
Wake on LAN
®
and PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) flash interface. Optional PCI
adapters offering failover and load balancing between adapters are available for added
throughput and increased system availability.
Ultra-Efficient Cooling
Six strategically located hot-swap/redundant fans, combined with efficient airflow paths,
provide highly effective system cooling for the eX4 systems, known as Calibrated Vectored
Cooling. The fans are arranged to cool three separate zones, left, center, and right, with one
pair of redundant fans per zone.
The fans automatically adjust speeds in response to changing thermal requirements, depending
on the zone, redundancy, and internal temperatures. When the temperature inside the server
increases, the fans speed up to maintain the proper ambient temperature. When the
temperature returns to a normal operating level, the fans return to their default speed. Why not
simply run the fans at 100% capacity all the time? For several good reasons: to reduce the
ambient noise, reduce the wear-and-tear on the fans and reduce the server power draw. The
reduction in ambient noise and power draw may be relatively minor for a single server, but if you
have a larger number of systems the aggregate savings in power and noise pressure can be
significant.
In addition, the server uses hexagonal ventilation holes in the chassis. Hexagonal holes can
be grouped more densely than round holes, providing greater airflow through the system cover.
This cooling scheme is important because newer, more powerful processors generate a
significant amount of heat, and heat must be controlled for the system to function properly.
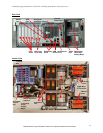
Hot-Swap/Redundant Components
System availability is maximized through the extensive use of hot-swap and redundant
components, including:
• Hot-add/hot-swap redundant memory protection (with Chipkill, Memory ProteXion,
and selectable memory mirroring capabilities)
• Hot-swap redundant hard disk drives (with standard LSI 1078 controller and optional
ServeRAID-MR10k providing multiple levels of RAID support)
• Hot-swap PCIe adapter slots (with optional failover support)
• Hot-swap redundant cooling fans (three redundant pairs)
• Hot-swap redundant power supplies
4
Light Path Diagnostics
Light path diagnostics enables a technician to quickly identify and locate a failed or failing
system component, such as a specific memory DIMM. (Monitored components include
processors, memory, power supplies, fans, HDDs, adapters, and voltage regulator modules
(VRMs), plus system temperature.) This enables quick replacement of the component, which
helps increase server uptime and lower operating costs.
The front of the server has an LED indicator light to show possible component failures. If the
2
Variable read rate. Actual playback speed varies and is often less than the maximum possible.
3
Actual throughput will depend on the adapter vendor’s implementation.
4
At 220V both power supplies are redundant; at 110V only the first power supply is redundant.