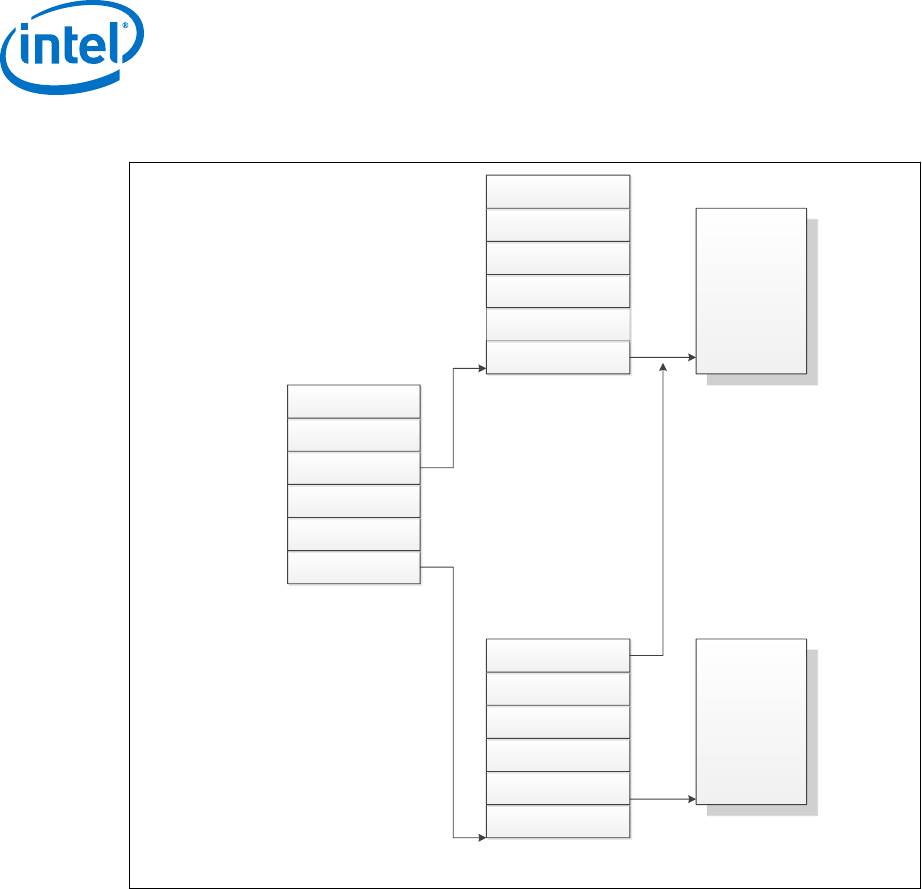
Figure 10. Device to Domain Mapping Structures
Root entry 0
Root entry N
Root entry 255
Context entry 0
Context entry 255
Context entry 0
Context entry 255
(Bus 255)
(Bus N)
(Bus 0)
Root entry table
(Dev 31, Func 7)
(Dev 0, Func 1)
(Dev 0, Func 0)
Context entry Table
For bus N
Context entry Table
For bus 0
Address Translation
Structures for Domain A
Address Translation
Structures for Domain B
Intel VT-d functionality, often referred to as an Intel VT-d Engine, has typically been
implemented at or near a PCI Express host bridge component of a computer system.
This might be in a chipset component or in the PCI Express functionality of a processor
with integrated I/O. When one such Intel VT-d engine receives a PCI Express
transaction from a PCI Express bus, it uses the B/D/F number associated with the
transaction to search for an Intel VT-d translation table. In doing so, it uses the B/D/F
number to traverse the data structure shown in the above figure. If it finds a valid
Intel VT-d table in this data structure, it uses that table to translate the address
provided on the PCI Express bus. If it does not find a valid translation table for a given
translation, this results in an Intel VT-d fault. If Intel VT-d translation is required, the
Intel VT-d engine performs an N-level table walk.
For more information, refer to Intel
®
Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O
Architecture Specification http://download.intel.com/technology/computing/vptech/
Intel(r)_VT_for_Direct_IO.pdf
Intel
®
VT-d Features
The processor supports the following Intel VT-d features:
Processor—Technologies
Desktop 4th Generation Intel
®
Core
™
Processor Family, Desktop Intel
®
Pentium
®
Processor Family, and Desktop Intel
®
Celeron
®
Processor Family
Datasheet – Volume 1 of 2 December 2013
42 Order No.: 328897-004


















