Serial Interfaces
Connecting the Serial Interfaces
Panasonic Semiconductor Development Company MN102H75K/F75K/85K/F85K LSI User Manual
128
Panasonic
5.3 Connecting the Serial Interfaces
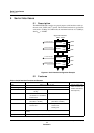
Figures 5-2, 5-3, and 5-4 illustrate six different methods of connecting the serial
interface.
5.3.1 Synchronous Serial Mode Connections
See section 11, “I/O Ports,” for
details on setting up the SBT
port.
Figure 5-2 shows serial port connections for either simplex or full-duplex syn-
chronous serial transfers.
5.3.2 UART Mode Connections
Figure 5-3 shows serial port connections for either simplex or full-duplex UART
transfers.
5.3.3 I
2
C Mode Connection
The serial interfaces can connect to I
2
C slave transmitters or receivers. For this
mode, always pull up the SBO and SBT pins to V
DD
. Either connect a pullup
resistor externally or turn on the internal one by setting the PPLU register.
A. Simplex Connection B. Full-Duplex Connection
Figure 5-2 Synchronous Serial Mode Connections
A. Simplex Connection B. Full-Duplex Connection
Figure 5-3 UART Mode Connections
Figure 5-4 I
2
C Mode Connection
SBO
SBI
SBO
SBI
SBT
SBT
Transmit
Receive
SBO
SBI
SBO
SBI
Transmit/receive
SBT
SBT
Transmit/receive
SBO
SBI
SBO
SBI
Transmit
Receive
SBO
SBI
SBO
SBI
Transmit/receive
Transmit/receive
SBO
SBT
Master
transmitter/
receiver
Slave
transmitter/
receiver
MN102H75K
Slave
transmitter/
receiver