Chapter 2 NI 4050 Operation
© National Instruments Corporation 2-5 NI 4050 User Manual
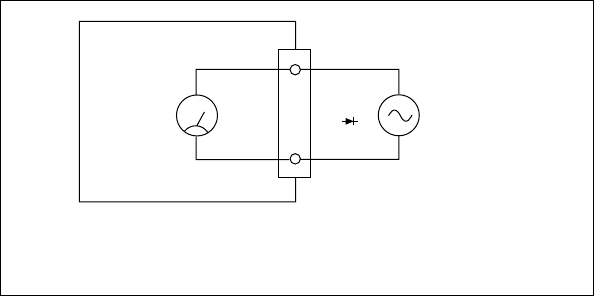
Figure 2-2. Normal Mode Measurement Effects
If you are measuring signals in the presence of large normal mode voltages,
consult Appendix A, Specifications, to calculate the additional error to your
system. Use the equation in Figure 2-2 to calculate the voltage error due to
normal mode voltage.
Common Mode Rejection
Common mode rejection (CMR) is the ability of the NI 4050 to reject
signals that are common to both input terminals. The ability is quantified in
the common mode rejection ratio (CMRR) specification. Theoretically, the
floating measurement circuitry of the NI 4050 should have an infinite
CMRR. Parasitic resistances and capacitances to earth ground limit the
CMR of the NI 4050. This effect is most noticeable when measuring small
signals in the presence of a large common mode voltage, as shown in
Figure 2-3.
Source
Voltage
V
s
at 60 Hz
+
–
Measured
Voltage
V
m
V
m
V
s
10
NMRR
–
20
--------------------
×=
HI
LO
Input
VΩ


















