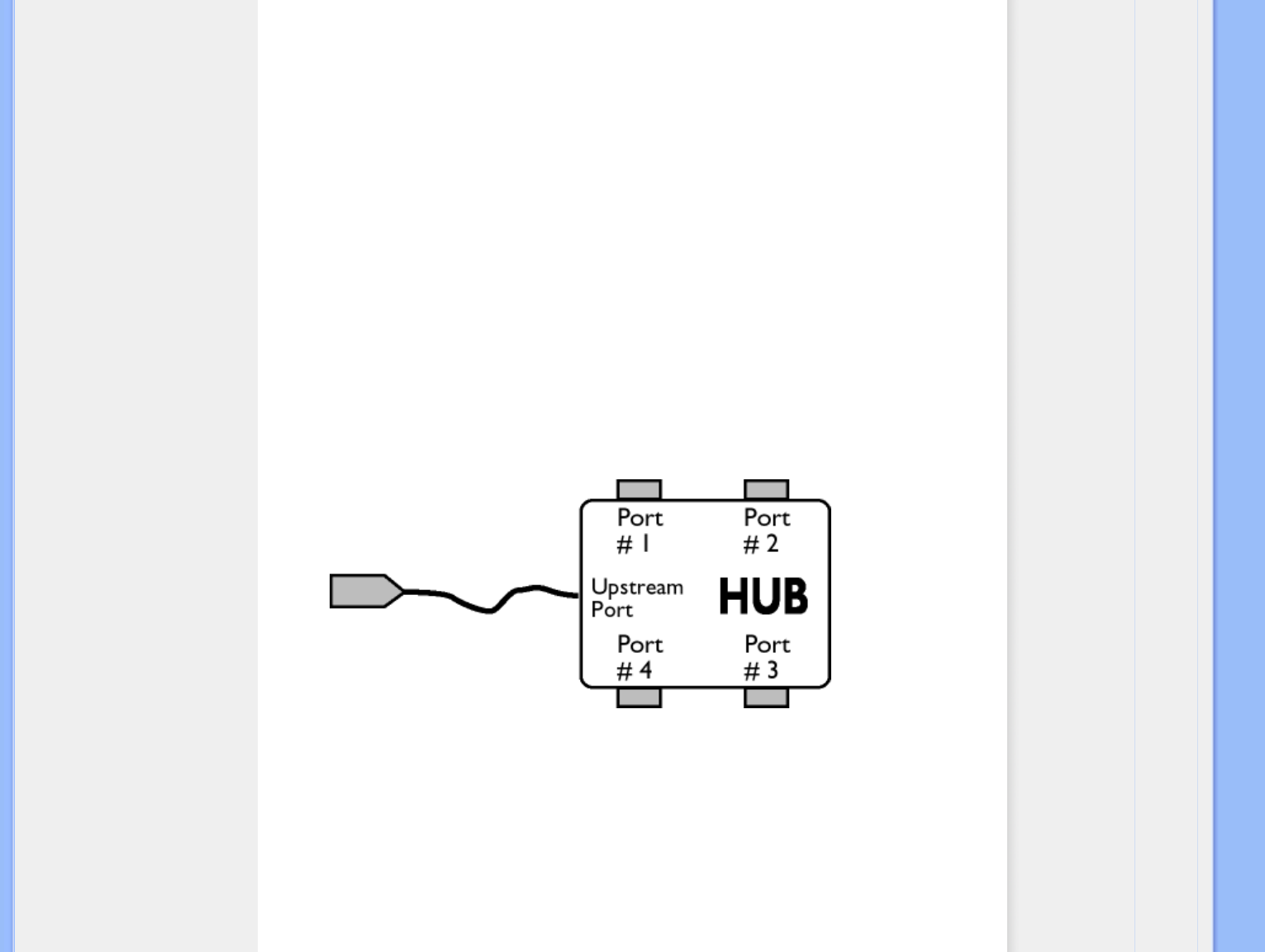
The upstream port of a hub connects the hub towards the host. Each of the other downstream ports
of a hub allows connection to another hub or function. Hubs can detect, attach and detach at each
downstream port and enable the distribution of power to downstream devices. Each downstream
port can be individually enabled and configured at either full or low speed. The hub isolates low
speed ports from full speed signaling.
A hub consists of two portions: the Hub Controller and Hub Repeater. The repeater is a protocol-
controlled switch between the upstream port and downstream ports. It also has hardware support
for reset and suspend/resume signaling. The controller provides the interface registers to allow
communication to/from the host. Hub specific status and control commands permit the host to
configure a hub and to monitor and control its ports.
Device
A logical or physical entity that performs a function. The actual entity described depends on the
context of the reference. At the lowest level, device may refer to a single hardware component, as
in a memory device. At a higher level, it may refer to a collection of hardware components that
perform a particular function, such as a Universal Serial Bus interface device. At an even higher
level, device may refer to the function performed by an entity attached to the Universal Serial Bus;
for example, a data/FAX modem device. Devices may be physical, electrical, addressable, and
logical.
Downstream
The direction of data flow from the host or away from the host. A downstream port is the port on a
hub electrically farthest from the host that generates downstream data traffic from the hub.
Downstream ports receive upstream data traffic.


















