23
7. Do not use the AUD full-trace mode for the VIO function.
8. If a completion-type exception occurs during exception branch acquisition, the next address to
the address in which an exception occurs is acquired.
Internal Trace Function:
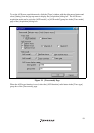
This function is activated by selecting the [Internal trace] radio button
in the [Trace type] group box of the [Trace mode] page. This function traces and displays the
branch instructions. The branch source address and branch destination address for the eight latest
branch instructions are displayed. See figure 2.1, [Trace mode] Page.
Notes: 1. If an interrupt is generated at the program execution start or end, including a step
operation, the emulator address may be acquired. In such a case, the following
message will be displayed. Ignore this address because it is not a user program
address.
*** EML ***
2. If a completion-type exception occurs during exception branch acquisition, the next
address to the address in which an exception occurs is acquired.
3. Trace information cannot be acquired for the following branch instructions:
• The BF and BT instructions whose displacement value is 0
• Branch to H'A0000000 by reset
4. The internal trace acquisition is not available when [User] is selected in the [UBC
mode] list box of the [Configuration] dialog box. In this case, close the [Trace]
window.
2.2.3 Notes on Using the JTAG (H-UDI) Clock (TCK) and AUD Clock (AUDCK)
1. Set the JTAG clock (TCK) frequency to lower than the frequency of the SH7339 peripheral
module clock (CKP).
2. Set the AUD clock (AUDCK) frequency to 50 MHz or lower. If the frequency is higher than
50 MHz, the emulator will not operate normally.
2.2.4 Notes on Setting the [Breakpoint] Dialog Box
1. When an odd address is set, the next lowest even address is used.
2. A BREAKPOINT is accomplished by replacing instructions of the specified address.
Accordingly, it can be set only to the internal RAM area. However, a BREAKPOINT cannot
be set to the following addresses:
• An area other than CS0 to CS6 and the internal RAM
• An instruction in which Break Condition 2 is satisfied
• A slot instruction of a delayed branch instruction
• An area that can be only read by MMU
3. During step operation, BREAKPOINTs are disabled.