SATA 150 RAID 2 Port PCI Host RC201 User Manual
1.1.2. High Speed Serial ATA Interface
Two special shielded and durable SATA1 connectors for plugging more than 1,000 times
Dual high speed Serial ATA interface ports, each supporting 1st generation Serial ATA
data rates (1.5Gb/s).
Provides RAID 0 (Stripping) to greatly increase the performance of data transfer by
simultaneously writing data to 2 drives.
Provides RAID 1 (Mirroring) to protect the data from a disk failure by writing identical data on 2
drives.
Fully compliant with Serial ATA 1.0 specifications.
Supports Spread Spectrum in receiver.
Independent 256-byte FIFOs (32 bit * 64 deep) per Serial ATA channel for host reads and writes.
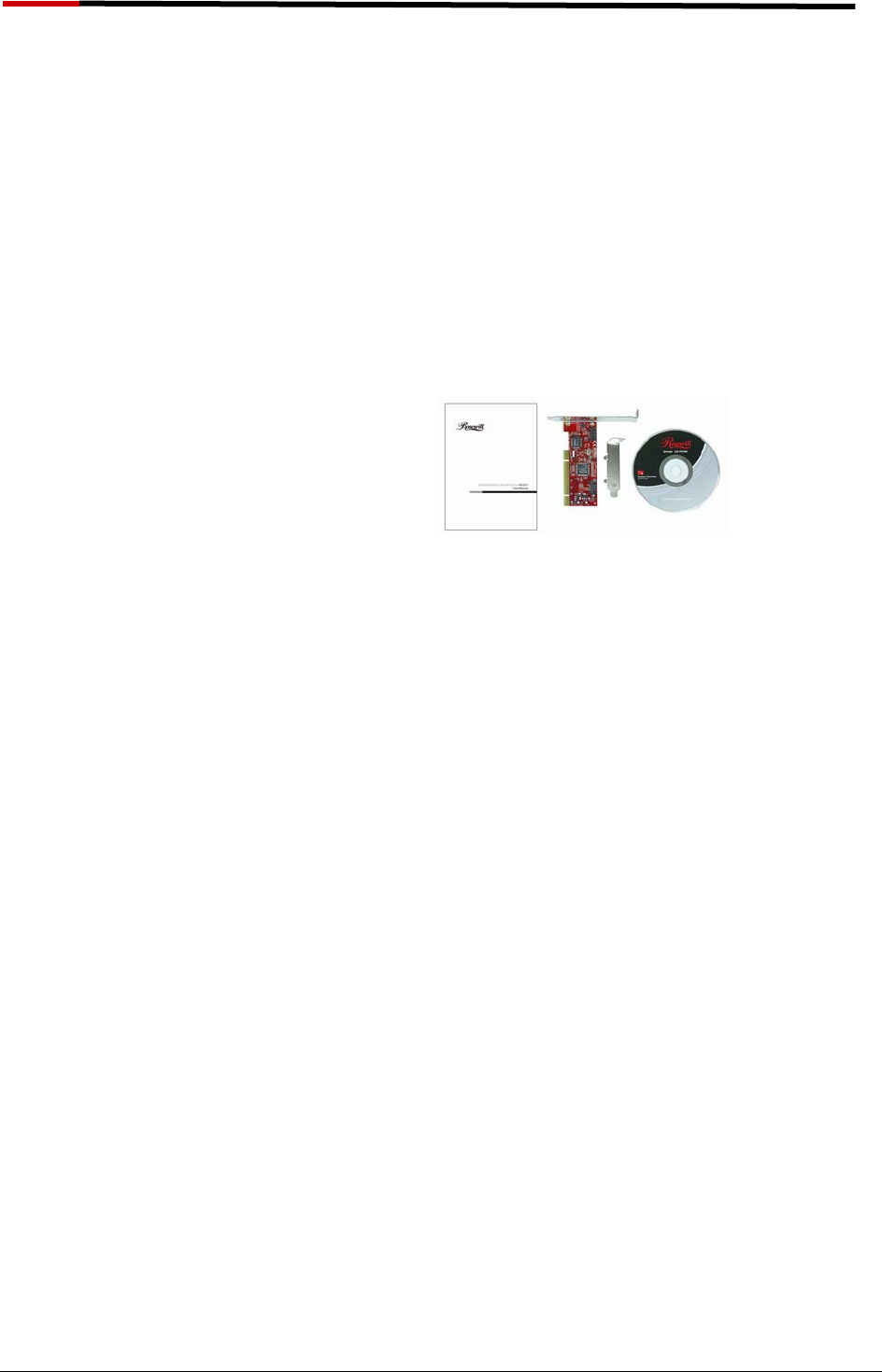
1.2. Package Contents
SATA RAID 2 Port PCI Host Adapter
Users Manual
Driver CD
Low profile bracket
2. What Is RAID
RAID or un-RAID function
RC-201 is designed for two functions- a RAID card with RAID 0/1 or an extending card for two SATA
devices with un-RAID. The un-RAID installation is the same as the RAID installation as below. The only
different is that you won’t need to enter the RAID BIOS to set a RAID structure.
If you want to use RC-201 as a un-RAID card, please do not enter the RAID BIOS and set any RAID set at
the beginning of booting. You can jump to P5 directly to complete the driver installation. The only different
is ignoring the step of RAID setting and the driver setting is the same as a RAID card.
RAID - Redundant Array of Independent Disks
RAID technology manages multiple disk drives to enhance I/O performance and provide redundancy in
order to withstand the failure of any individual member, without loss of data. This card provides two
RAID Set types, Striped (RAID 0) and Mirrored (RAID 1).
Disk Striping (RAID 0)
Striping is a performance-oriented, non-redundant data mapping technology. While Striping is discussed
as a RAID Set type, it is actually does not provide fault tolerance. With modern SATA bus mastering
technology, multiple I/O operations can be done in parallel, enhancing performance. Striping arrays
use multiple disks to form a larger virtual disk.
Disk Mirroring (RAID 1)
Disk mirroring creates an identical twin for a selected disk by having the data simultaneously written to two
disks. This redundancy provides instantaneous protection from a single disk failure. If a read failure occurs
on one drive, the system reads the data from the other drive.
3. BIOS Installation (RAID Setting)
Creating and deleting RAID sets is a function found in the BIOS. During boot up, the RAID setting message
will appear and pause for a few moments to allow the user to choose what to do. This board will act as
normal NON-RAID card when BIOS not configured for RAID. Just proceed to Software Installation
section directly. If you use traditional parallel ATA HDD, make sure your hard drives be set up as master
mode before the RAID setting.
3














