STH-DCAM USER’S MANUAL 2001 VIDERE DESIGN
4.6 Range Resolution
Range resolution is the minimum distance the stereo system can distinguish.
Since stereo is a triangulation operation, the range resolution gets worse
with increasing distance from the stereo head. The relationship is:
d
bf
r
r ∆=∆
2
,
where b is the baseline between the imagers, f is the focal length of the lens,
and
d
∆
is the smallest disparity the stereo system can detect. For the STH-
DCAM, b is 90 mm, and
d
∆
is 0.35 um (pixel size of 5.6 um, divided by
the interpolation factor of 16).
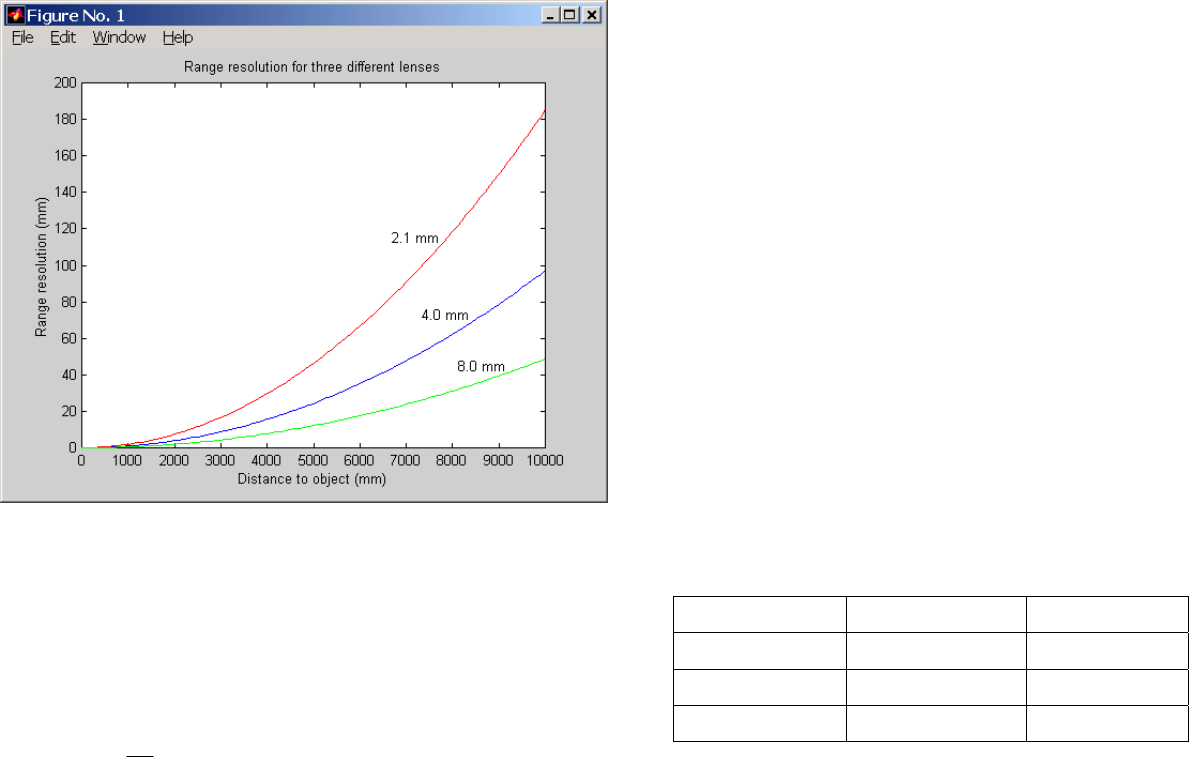
Figure 4-1 Range resolution in mm as a function of distance, for
several different lens focal lengths.
Figure 4-1 plots this relationship for several focal lengths. At any distance,
the range resolution is inversely proportional to the focal length.
4.7 Field of View
The field of view is completely determined by the focal length, given a
fixed imager. The formulas for the FOV in horizontal and vertical
directions are:
)/792.1arctan(2 fHFOV =
)/344.1arctan(2 fVFOV =
where f is in millimeters. For example, a 4.0 mm lens yields a horizontal
FOV of 48 degrees. The following table shows the FOV for some standard
focal lengths.
Lens focal length Horizontal FOV Vertical FOV
2.1 mm 81 deg 65 deg
4.0 48 37
8.0 25 19
Table 4-1 Horizontal and vertical field of view for
different lens focal lengths.
8