PMP3000 Models
Owner’s Manual
Welcome
This COLEMAN® product has been carefully engineered and manufactured to
give you dependable operation. Please read this manual thoroughly before
operating your new COLEMAN® product, as it contains the information you
need to become familiar with its features and obtain the performance that will
bring you continued enjoyment for many years. Please keep this manual on file
for future reference.
How Power Inverters Work
Power inverters convert low voltage DC (direct current) power to 120 volt AC
(alternating current) household power. This conversion process thereby
allows you to use household products, power tools, and other electronic
products away from normal AC power sources (standard 120V wall outlets).
Depending on the model and its rated capacity, inverters can draw power either
from standard 12-volt automobile and marine batteries or from portable high
power 12-volt power sources.
The waveform that is generated by this conversion is a “modified sine wave”.
The modified sine wave produced by our inverters has a root square mean
(RMS) voltage of 120 volts, which is the same as standard household power.
The majority of AC voltmeters are calibrated for RMS voltage under the
assumption that the measured waveform will be a pure sine wave. Therefore,
these meters will not read the RMS modified sine wave voltage correctly. They
will read about 20 to 30 volts too low. To accurately measure the output
voltage of the inverter, use a true RMS reading voltmeter such as a Fluke 87,
Fluke 8060A, Beckman 4410, Triplett 4200 or any voltmeter identified as a
“true RMS”.
Controls and Components
Front Panel
1. LED Indicator Light (Green = Power ON, Red = Overload)
2. Remote Control Connection
3. ON/OFF Power Switch
4. Digial Display
5. Display Selector Switch
6. 120 Volt AC Outlets
1
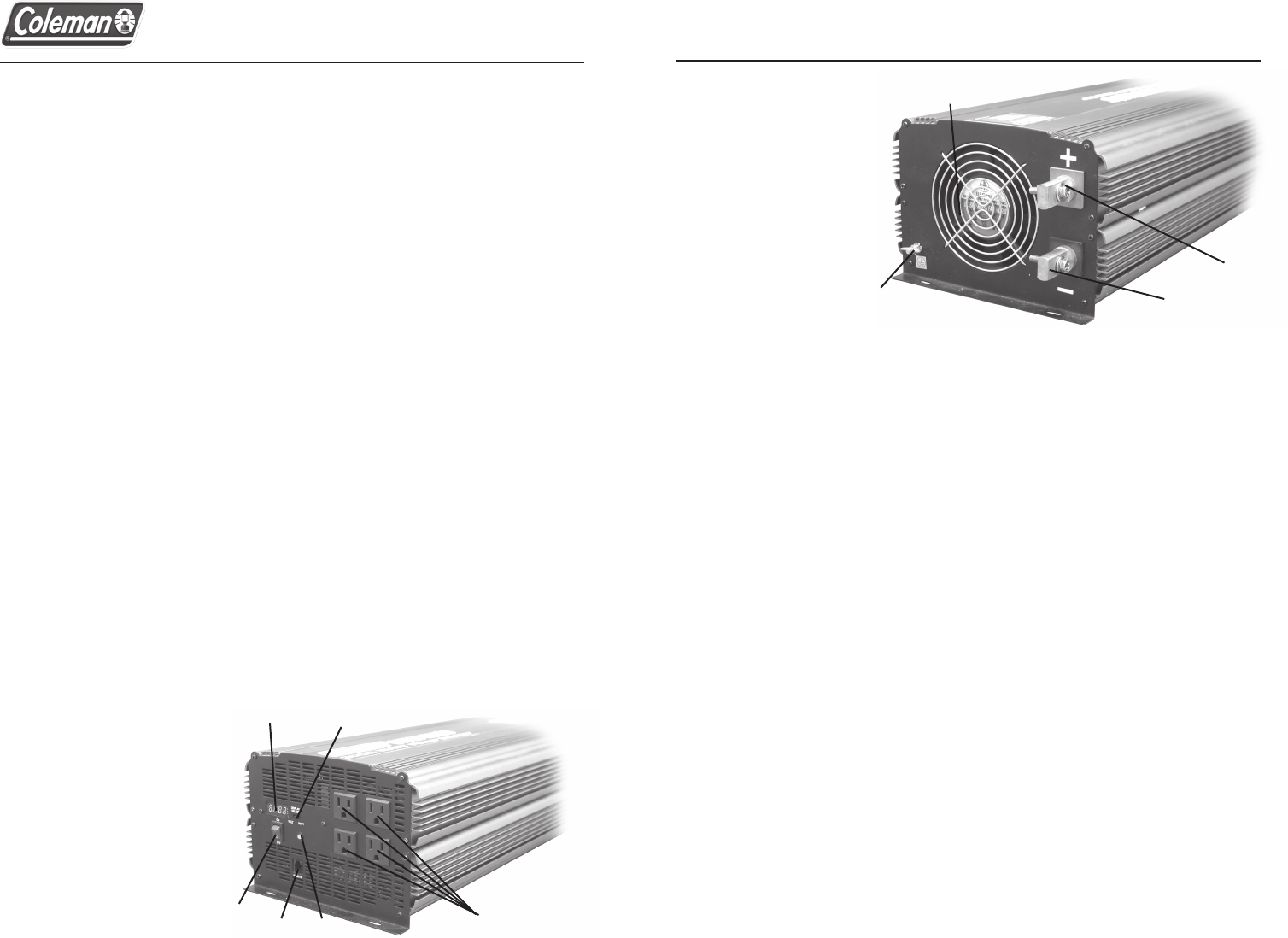
Rear Panel
7. Power Input Terminal
Red = Positive
8. Power Input Terminal
Black = Negative
9. Ground Lug Terminal
10. Cooling Fan
CAUTION
• The inverter is designed to operate from a 12-volt power source only. The unit
will not operate from a 6-volt battery or a 24-volt battery. Do not attempt to
connect the inverter to any other power source other than a battery
with a nominal output voltage of 12 volts or damage to the unit may
occur and will void the warranty.
• 120 volts can inflict serious injury, damage or death. Improper use of the in-
verter may result in property damage, personal injury or loss of life.
Getting Started
When you turn on an appliance or tool that operates using a motor or a tube
(such as a television), it requires an initial surge of power to start up. This surge
of power is referred to as the “starting load” or “peak load”. Once started, the
appliance or tool requires less power to continue to operate. This is referred to
as the “continuous load”.
You will need to determine how much power your appliance or tool requires
to start up (peak power) and it’s continued operating power requirements
(continuous load).
Power consumption is rated in either wattage (watts) or amperes (amps). This
information is usually stamped or printed on most appliances and equipment.
If this information is not indicated on the actual product, check the owner’s
manual or contact the manufacturer to determine the power consumption. Be
sure that the power consumption of the item you wish to operate is rated at
3000 watts or less.
Multiply: AMPS x 120 (AC voltage) = WATTS
This formula yields a close approximation of the continuous load of the
appliance.
To determine whether the inverter will operate a particular item, run a test. All
COLEMAN® inverters are designed to automatically shut down in the event of
a power overload. This protection feature prevents damage to the unit while
testing items with ratings in the 3000-watt range.
2
8
7
10
9
6
2
3
5
1
4








