TD-8816 ADSL2/2+ Ethernet Router User Guide
26
4.4.3.3. IP Address Mapping
Choose “Advanced Setup→NAT→IP Address Mapping” in Figure 4-16, you can configure the
Address Mapping Rule in the next screen. The IP Address Mapping is for those VCs that
configured with multiple IPs. The IP Address Mapping rule is per-VC based (only for Multiple IPs'
VCs).
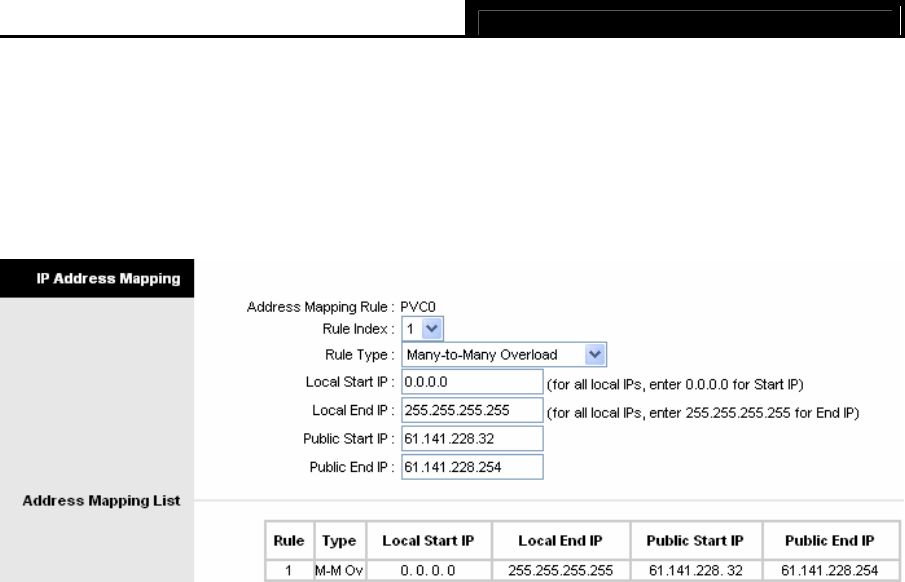
Figure 4-19
¾ Rule Index: Select the Virtual server rule index for this VC. You can specify 10 rules in
maximum. All the VCs with single IP will use the same Virtual Server rules.
¾ Rule Typ: There are four types of one-to-one, Many-to-One, Many-to-Many Overload and
Many-to-Many No-overload.
¾ Local Start & End IP: Enter the local IP Address you plan to mapped to. Local Start IP is the
starting local IP address and Local End IP is the ending local IP address. If the rule is for all
local IPs, then the Start IP is 0.0.0.0 and the End IP is 255.255.255.255.
¾ Public Start & End IP: Enter the public IP Address you want to do NAT. Public Start IP is the
starting public IP address and Public End IP is the ending public IP address. If you have a
dynamic IP, enter 0.0.0.0 as the Public Start IP.
¾ Address Mapping List: This displays the information about the Mapping addresses.
To add a mapping rule:
Step 1: Select the “Virtual Circuit” and Multiple for the “Number of IPs”. Then select the tab IP
Address Mapping for the Virtual server (shown in Figure 4-16)..
)
Note:
IP Address Mapping is only available for VCs with Multiple IPs.
Step 2: Select the Rule index for the rule as shown in Figure 4-19.
Step 3: Select the rule type you want from the drop-down list.
Step 4: Enter the local and public IP addresses in the corresponding fields.
Step 5: After that, click SAVE to make the entry take effect.
Other configurations for the entries as shown in Figure 4-19:
Enter the index of assigned entry, click the DELETE button to delete the entry.


















