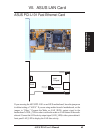
ASUS P5A User’s Manual 67
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
Glossary
Glossary
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
An interface specification that enables high-performance 3D graphics on mainstream
PCs. AGP offers a higher throughput than PCI by providing the graphics controller
with direct access to system memory.
Bus Bus Frequency Bus Speed
PCI 33MHz 133MB/s
AGP 1X 66MHz 200-300MB/s
AGP 2X 133MHz 528MB/s
AGP 4X 266MHz 1 GB/s
AUTOEXEC.BAT
AUTOEXEC.BAT is a special-purpose file that is automatically executed by DOS
whenever the computer is turned ON or restarted. This file contains important com-
mands that help configure the system to work with certain software and devices.
Windows 95 and later has its own startup files and may not use or may ignore parts
of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)
BIOS is a set of routines that affect how the computer transfers data between com-
puter components, such as memory, disks, and the display adapter. The BIOS in-
structions are built into the computer’s read-only memory. BIOS parameters can be
configured by the user through the BIOS Setup program. The BIOS can be updated
using the provided utility to copy a new BIOS file into the EEPROM.
Bit (Binary Digit)
Represents the smallest unit of data used by the computer. A bit can have one of two
values: 0 or 1.
Boot
Boot means to start the computer operating system by loading it into system memory.
When the manual instructs you to “boot” your system (or computer), it means to turn
ON your computer. “Reboot” means to restart your computer. When using Windows
95 or later, selecting “Restart” from “Start | Shut Down...” will reboot your computer.
Bus Master IDE
PIO (Programmable I/O) IDE requires that the CPU be involved in IDE access and
waiting for mechanical events. Bus master IDE transfers data to/from the memory
without interrupting the CPU. Bus master IDE driver and bus master IDE hard disk
drives are required to support bus master IDE mode.