9. DATA COMMUNICATIONS CONFIGURATIONS
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 8 described how DTEs and LANs can communicate through your communications system. In
addition, it told you how your communications system could communicate over greater distances using any
of the ACCUNET data services. This chapter integrates chapter 7 and 8 information by showing you how
you can configure your networks to:
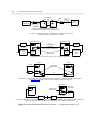
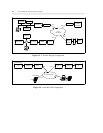
• Use the dedicated switched connection (DSC) and permanent switched connection (PSC) capabilities
of your communications system.
• Link SNA nodes through your communications system.
• Connect your local communications systems over public or private data networks for file transfers,
video teleconferencing, image processing, and FAX transmittal.
Note that the illustrations shown in this chapter depict only some of the many possible configurations
appropriate for a particular application. The configuration you install will depend upon the actual DTEs
and DCEs you use in the connection. When configuring a connection, remember to refer to table 1-7 and
tables 8-1 through 8-3 to determine the type of DCE that is appropriate. Other general rules that may help
you in your DCE decision are:
• When you send 56-kbps, robbed-bit data over a switched digital network, use the MPDM with the
ACCUNET modification kit. This MPDM is sometimes called the MPDM/M1* or the ACCUNET MPDM.
• In addition, if the destination DCE does not do a mode 2 handshake, you also should use the ACCUNET
MPDM (MPDM/M1*), regardless of whether you route the data through a switched digital network.
9-1