TRANSMISSION TYPES
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
Both analog and digital transmission can be used to carry information across telephone lines and data links.
ANALOG TRANSMISSION
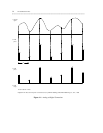
Analog transmission carries information as continuously varying electrical waves. Variables like the wave
amplitude, phase, and frequency impart the information contained in the signal.
Analog transmission can carry both voice and data.
• Voice: Since voice originates as analog sound waves, analog voice terminals can transmit it over analog
facilities without any conversion.
VOICE TERMINAL
VOICE
(SOUND WAVES)
ANALOG
SIGNAL
• Data: The discrete binary pulses that are generated by digital terminal equipment cannot be carried
across analog lines. However, they can be used to vary (modulate) a carrier signal, which analog
facilities can carry. At the destination, the variation in the signal is mapped to the original binary pulses
(demodulated), and the original pulses are regenerated. Modems perform this modulation/demodulation
function.
The analog facilities over which voice and modulated data are carried are sometimes called voice-grade
lines. Hence, the name voice-grade data has been used for data carried over analog facilities.
MODEM
DATA (BINARY
VOLTAGE PULSES)
ANALOG
SIGNAL
(CARRIER
FREQUENCY)
DIGITAL TRANSMISSION
Digital transmission carries information as discrete pulses transmitted at different voltage levels (for
example, +3 volts/−3 volts). Each pulse represents a binary bit (for example, a +3-volt pulse might
represent a binary 1, while a −3-volt pulse might represent a binary 0). The bits are grouped into 8-bit units
called bytes that convey the information. Like analog transmission, digital transmission can carry both
voice and data.
1-3