PUBLIC AND PRIVATE DATA NETWORK CONNECTIONS 8-23
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
• Image viewing and transfer — Using slow-scan and freeze-frame capabilities, SDS and SDDN let
senders and receivers jointly study databases, engineering drawings, and X-rays.
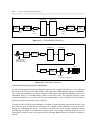
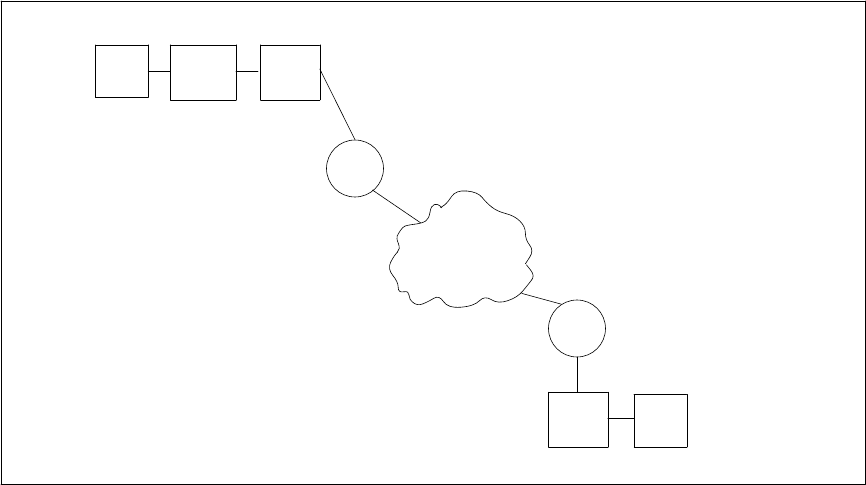
Connections to the Public SDN/SDDN Circuit-Switched Data Network
Requirements for connections from a PBX DS1 port to a public network destination through SDS or SDDN
vary according to the type of signaling used (that is, robbed-bit or ISDN-PRI MOS), and the data speed.
Data speed is set at the originating and destination data modules in the following DMI modes:
• Mode 0 — 64-kbps synchronous transmission (PRI)
• Mode 1 — 56-kbps synchronous transmission (robbed-bit or PRI)
• Mode 2 — up to 19.2-kbps asynchronous transmission (PRI)
• Mode 3 — 64-kbps packet data (PRI)
Figures 8-14 through 8-16 show some typical connections through both the domestic and international
SDS/SDDN network. Table 8-6 lists the requirements for the illustrated connections.
SW56K
DSU
MPDM/M1*
OR
7500B
DTE
PUBLIC
SWITCHED
DATA NETWORK
S75/S85
G1/G2
DTE
SW56 SERVICE
DS1 WITH
SW56 SERVICE
(ROBBED BIT)
POP
POP
4ESS
4ESS
Figure 8-14. Public Switched Data Network with Robbed Bit Facilities (Mode 1)