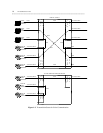
TRANSMISSION STATES 1-13
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
Protocols Used
The following is a list of the protocols that are meaningful when you transmit data to and through the
switch. The list is organized by protocol layers. As you read through the list, follow the protocol changes
through the transmission paths shown in figure 1-3.
Layer 1 Protocols
Layer 1 standards include those used between the terminal or host (DTE) and the data communications
equipment (DCE), those used between the DCE and the switch port, and those used inside the switch.
The following are the layer 1 protocols used between the DTE and the DCE. DCEs can be data modules,
modems, or data service units (DSUs*).
• RS-232C — A common physical interface used to connect a DTE to a DCE. This protocol is typically
used for communicating up to 19.2 kbps.
• RS-449 — A replacement specification for RS-232C. It was devised to overcome the RS-232C distance
and speed restrictions, and the lack of modem control that RS-232C procedures afford.
• V.35 — A physical interface used to connect a DTE to a DCE. This protocol is typically used for
transmissions at 56 or 64 kbps.
The following protocols constitute the conventions used at layer 1 to govern communication between the
DCE and the port. These protocols consist of codes that are inserted at the originating DCE and stripped at
the switch port. The DS1 protocol may be inserted at the originating, outgoing trunk port and stripped at
the destination port.
• Digital communications protocol (DCP) — An AT&T proprietary standard for a 3-channel link. The
DCP channel structure consists of two information channels and one signaling channel (2I+1S). Each I
channel provides 64 kbps of voice/data communication, while the S channel provides 8 kbps of
signaling communication. DCP protocol is similar to the ISDN basic rate interface (BRI). In fact,
AT&T created DCP in anticipation of the ISDN-BRI standard. Digital voice terminals that interface
with the System 75, System 85, and DEFINITY Generic 1 and 2 systems use this protocol for
communications. See appendix D for further details.
• Basic rate interface (BRI) — An ISDN standard for a 3-channel link, consisting of two 64-kbps bearer
(B) channels and one 16-kbps signaling (D) channel. For the AT&T implementation of this standard,
see DEFINITY Communications System and System 75 and System 85 ISDN BRI Reference (555-025-
102).
• Analog — A modulated carrier signal.
• ADU Proprietary — A signal generated by an Asynchronous Data Unit (ADU). The signal has been
designed for communication over limited distances and can be understood only by a destination ADU
or destination switch port with a built-in ADU.
• DS1 — A protocol that dictates the line coding, signaling, and framing used on a 24-channel line. (See
the Multiplexed Communication section of this chapter for an explanation of these parameters.) Many
__________________
* A DSU is a device designed to transmit digital data to a particular digital endpoint over the public network without processing it
through any intervening private network switches.