29
29
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
section
Using the Belkin Wireless LAN Utility
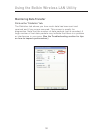
(f) Client IP Address
Shows the IP address of the computer. The IP address is obtained
automatically by default. You may set the IP address manually through
Windows Networking Properties.
(g) Network Connection Type
Shows the current wireless mode the Card is operating in. There are
two operating modes: Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc. Infrastructure is the
most common mode to operate in. Infrastructure mode is used when
connecting your PC to a wireless router or a wireless access point.
Ad-Hoc mode is used to connect two or more computers together
without the use of a wireless router or an access point.
(h) Radio State
Shows whether the radio of your wireless client is enabled or
disabled.
(i) Signal
Displays the wireless signal strength in decibels (dBm). The decibel
scale is negative, so smaller absolute values correspond to stronger
signals (i.e. -20 dBm is stronger than -80 dBm). The signal to noise
ratio (SNR) is the difference between the signal and the noise (e.g.
if the noise is -80 dBm and the signal is -20 dBm, the SNR is 60
dB); the larger the SNR, the better. In general, connections should
have an SNR greater than 20 dBm, or the user may experience poor
reliability and/or performance. If the signal is less than -50 dBm, the
user should consider repositioning their workstation Wireless Router
or Access Point, rotating the Wireless Router or Access Point’s
antennas, or Limiting their Transmission Rate (described on page 38
of the troubleshooting section of the manual), to ensure a reliable
wireless connection.
(j) Noise
Displays the intensity of the external noise, on this wireless channel,
in decibels (dBm). If the noise is greater than -70 dBm, the user
should consider changing the wireless channel used in their Wireless
Router or Access Point, to ensure a reliable wireless connection.