33
33
section
1
2
3
4
5
6
Troubleshooting
What’s the difference between 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11a,
and Pre-N?
Currently there are four levels of wireless networking standards, which
transmit data at very different maximum speeds. Each is based on
the designation for certifying network standards. The most common
wireless networking standard, 802.11b, transmits information at
11Mbps; 802.11a and 802.11g work at 54Mbps; and Pre-N works
at 108Mbps. Pre-N, the precursor to the upcoming 802.11n release,
promises speeds that exceed 802.11g, and up to twice the wireless
coverage area. See the following chart for more detailed information.
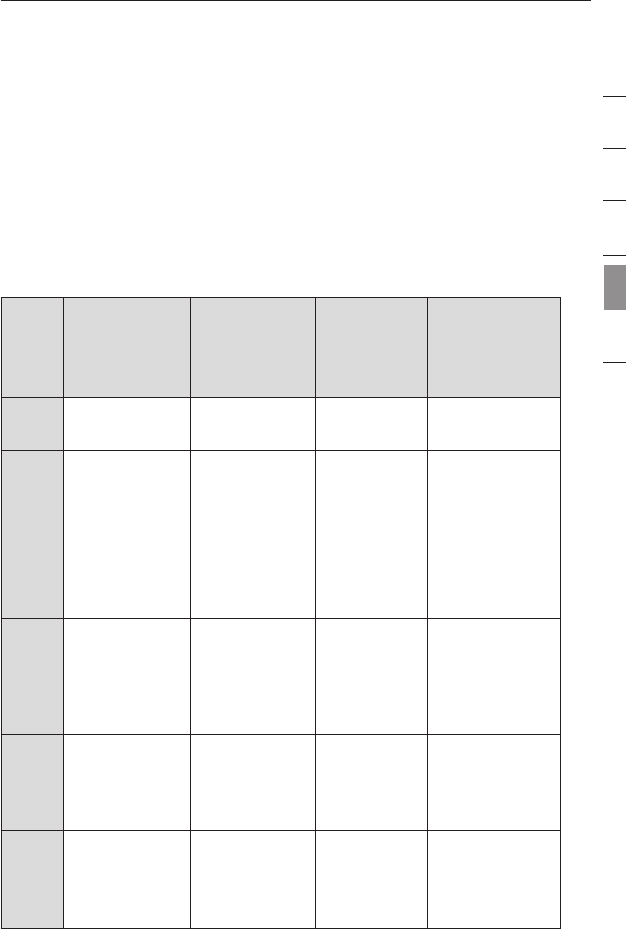
Wireless Comparison Chart
Wireless
Technology
802.11b
802.11g
802.11a
Belkin
Pre-N
Speed 11Mbps 54Mbps
54Mbps
600% faster
than standard
802.11g*
Frequency
Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens may
interfere with the
unlicensed band
2.4GHz
Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens may
interfere with the
unlicensed
band 2.4GHz
5GHz—
uncrowded
band
Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens may
interfere with the
unlicensed
band 2.4GHz
Compatibility
Compatible
with 802.11g
Compatible
with 802.11b
Incompatible
with 802.11b
or 802.11g
Compatible with
802.11g
or 802.11b
Coverage*
Depends on
interference—
typically
100–200 ft.
indoors
Depends on
interference—
typically
100–200 ft.
indoors
Interference
range is
typically 50–
100 ft.
Up to 800% wider
coverage than
standard 802.11g*
Advantage
Mature—legacy
technology
Common—
widespread
use for Internet
sharing
Less
interference—
great for
multimedia
application
Leading edge—
best coverage
and throughput
*Distance and connection speeds will vary depending on your networking environment.