35
_______________________________________________________________________________________APPLICATIONS
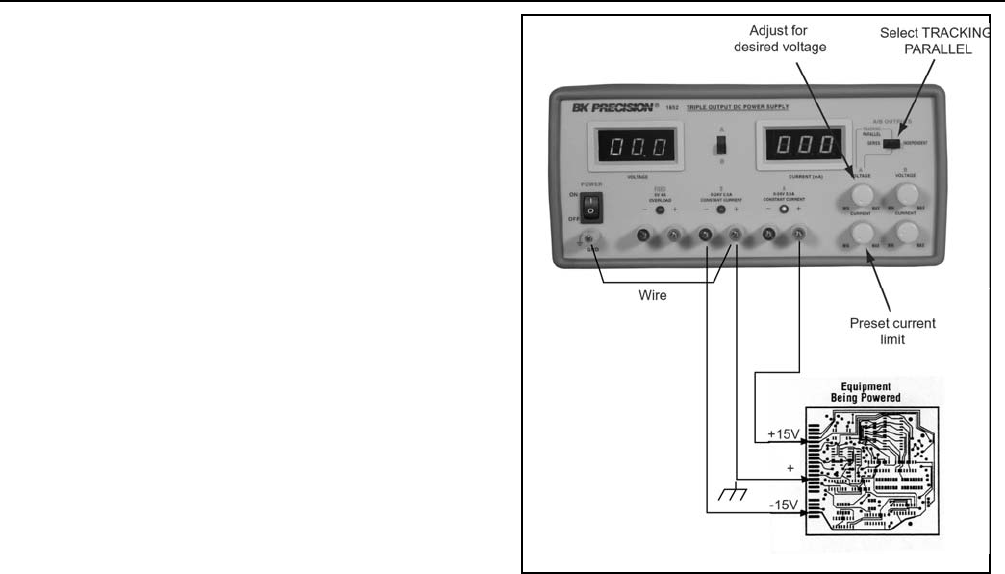
Identical Positive and Negative Voltages With a
Separate Common (Refer To Fig. 15)
Another typical “split supply” application is when a circuit
uses operational amplifiers (op-amps). Typically, identical
positive and negative voltages are required to power op-amp
circuits. Using both supplies and the series tracking mode of
operation, identical positive and negative voltages with a
separate common are obtained as follows:
1. Select the Tracking Series operating mode and set A/B
Metering switch to monitor the “A” supply.
2. Set the desired voltage using the “A” VOLTAGE
controls.
3. Connect a ground wire between the “A” supply negative
terminal and the GND (green) terminal.
4. Turn off the power supply and the equipment to be
powered during hook-up.
5. Connect the positive polarity input of the circuit to be
powered to the positive (red) terminal of the “A” supply
and connect the negative polarity of the circuit to the
negative terminal of the “B” supply. Connect the circuit
ground to the ground terminal of the “A” supply, the
positive terminal of the “B” supply, or the GND (green)
terminal.
Fig. 15. Typical Hook-Up Using Identical Positive
and Negative Voltages with a Separate Common.