Network Design
5-12 Creating a Manageable Plan
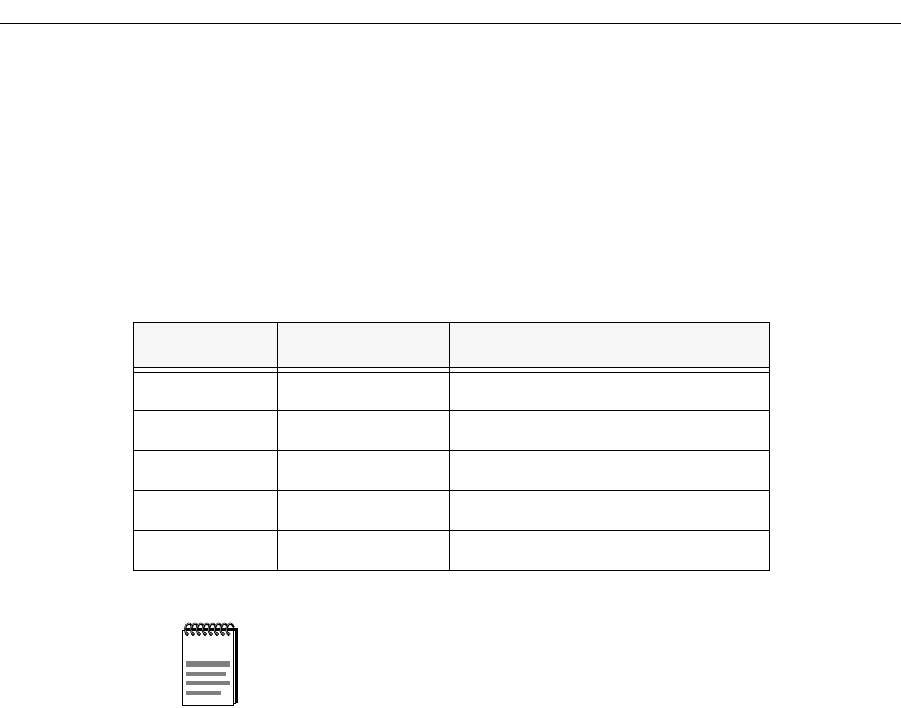
Use a standard, decipherable labeling code for cable and hardware. A label
reading L2N5W2C1S243 may look like gibberish now, but if you know that
the letter codes indicate locations or conditions of installation, it can be quite
helpful. Table 5-1, below, shows the meanings of the codes and numbers of
this example.
Cable Label: L2N5W2C1S243
Fault Aversion
A good network design strategy realizes the importance of avoiding future
trouble spots. It is possible to design a network such that the most dangerous of
these trouble spots are either eliminated, covered by contingencies, or their effects
are minimized. This aspect of network design is called “fault aversion.”
A fault averse network uses the capabilities of available hardware and the
fault-tolerance or recovery features of the technologies of the network to provide
for three things: the elimination of single points of failure, the availability of
redundancy, and the quick and easy isolation of and recovery from errors or
problems.
Table 5-1. Cable Code Key
Code Code Definition Meaning
L2 Location 2 Engineering Building
N5 Network 5 Network Map #5
W2 Workgroup 2 Production Controls Workgroup
C1 Closet 1 Wiring Closet #1
S243 Station 243 Wallplate #243
NOTE
The code key depicted above is only an example, and is not
indicative of any industry standard or generally accepted cable
marking practices.


















