Appendix B: Bridging Methods
Page B-2 Token Ring Switch Module User Guide
B.2 TRANSPARENT BRIDGING
Transparent or spanning tree bridging requires no initial programming.
After being installed on the network, they “learn” and remember the
location of the attached devices by reading the source addresses of
incoming packets. Then they place the source address and port
information in a lookup table.
When a packet comes into a port, the bridge reads the destination address
and attempts to find the location of the destination node using its lookup
table. If the address is in the table, the bridge simply re-transmits the
packet out of the appropriate port. If the address is not found in the table
the bridge re-transmits the packet out of all the ports except the source
port.
Transparent or spanning tree bridges also usually provide some packet
filtering capabilities. On some networks it is desirable to prevent certain
stations from accessing other segments. The ATX uses this bridging
method.
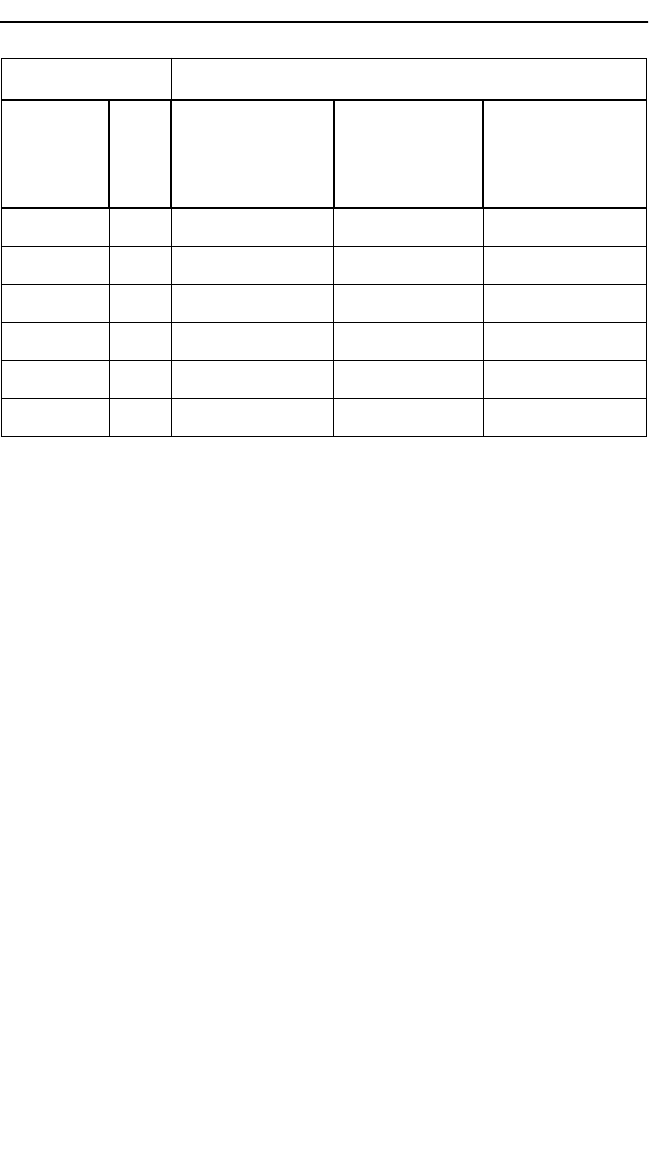
a. source address is not learned
Exit Port Configuration
Entry
Port
Config.
RII
SRT
(Source
Routing
Transparent)
SR
(Source
Routing)
TST
(Transparent
Spanning
Tree)
SRT 0 spanning tree block spanning tree
1 source route source route spanning tree
a
SR 0 block block block
1 source route block block
TST 0 spanning tree block spanning tree
1 spanning tree
a
block spanning tree
a


















