ț27ț
•You cannot use scientific functions in binary, octal, deci-
mal, and hexadecimal calculations. You cannot input val-
ues that include decimal part and an exponent.
• If you input a value that includes a decimal part, the unit
automatically cuts off the decimal part.
•Negative binary, octal, and hexadecimal values are pro-
duced by taking the two's complement.
•You can use the following logical operators between
values in Base-
n calculations: and (logical product), or
(logical sum), xor (exclusive logical sum), xnor (exclu-
sive logical sum negation), Not (negation), and Neg (mi-
nus).
• The following are the allowable ranges for each of the
available number systems.
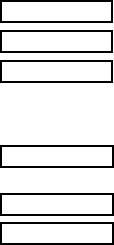
Binary 1000000000 Ϲ
x Ϲ 1111111111
0 Ϲ
x Ϲ 0111111111
Octal 4000000000 Ϲ
x Ϲ 7777777777
0 Ϲ
x Ϲ 3777777777
Decimal –2147483648 Ϲ
x Ϲ 2147483647
Hexadecimal 80000000 Ϲ
x Ϲ FFFFFFFF
0 Ϲ
x Ϲ 7FFFFFFF
• Example 1: To perform the following calculation and
produce a binary result:
10111
2
+ 11010
2
Binary mode F F 3 b
0.
b
10111
2
+ 11010
2
0.
b
=
110001.
b
• Example 2: To perform the following calculation and
produce an octal result:
7654
8
÷ 12
10
Octal mode F F 3 o
0.
o
l l l 4
(
o
)
7654
8
\
l l l 1
(d)12
10
0.
o
=
516.
o


















