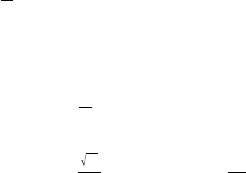
E-22
•Press the number key (1, 2, or 3) that corresponds to the angle unit
you want to use.
(90° =
radians = 100 grads)
• Example 1: sin 63°52o41ǥ ҃
0.897859012
q
.....
1
(
Deg)
S 63 I 52 I 41 I <
• Example 2: cos
(
rad
)
҃
0.5
q
.....
2
(
Rad)
W R A x \ 3 T <
• Example 3: cos
Ҁ1
҃
0.25
π (rad)
(
҃ (rad)
)
q ..... 2 (Rad)
A V R L 2 \ 2 T < g \ A x <
• Example 4: tan
Ҁ1
0.741 ҃
36.53844577
° q
.....
1
(
Deg)
A g 0.741 <
kHyperbolic/Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
• Example 1: sinh 3.6 ҃
18.28545536
M S 3.6 <
• Example 2: sinh
Ҁ1
30 ҃
4.094622224
M A j 30 <
kCommon and Natural Logarithms/Antilogarithms
• Example 1: log 1.23 ҃
0.089905111
R 1.23 <
• Example 2: In 90 (= log
e
90) =
4.49980967
T 90 <
ln e ҃
1
T p P <
• Example 3: e
10
҃
22026.46579
A U 10 <
• Example 4: 10
1.5
҃
31.6227766
A Q 1.5 <
• Example 5: (–2)
4
҃
16
R D 2 T W 4 <
•Negative values included in a calculation must be enclosed in parentheses.
For details, see “Order of Operations” on page 47 for more information.
π
2
π
3
π
4
2
2


















